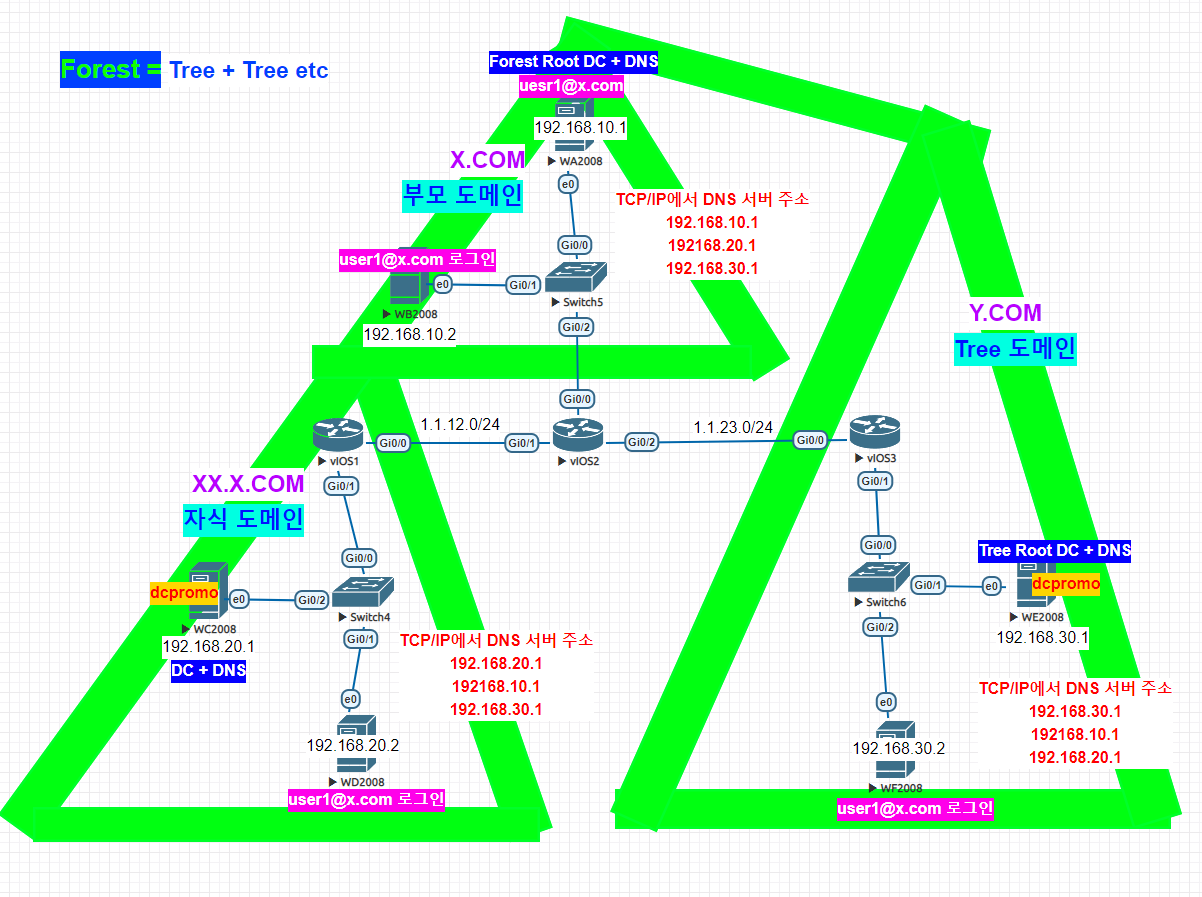
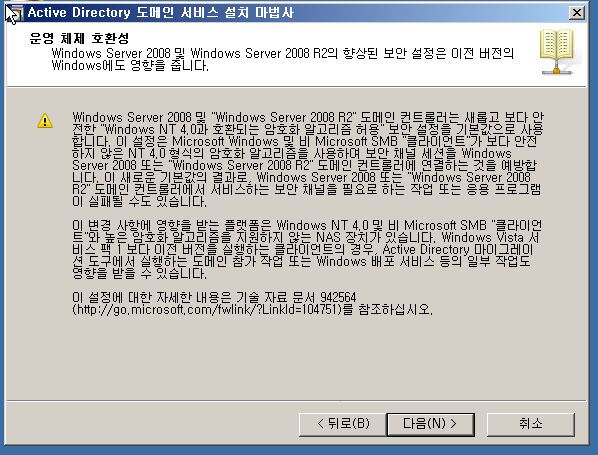
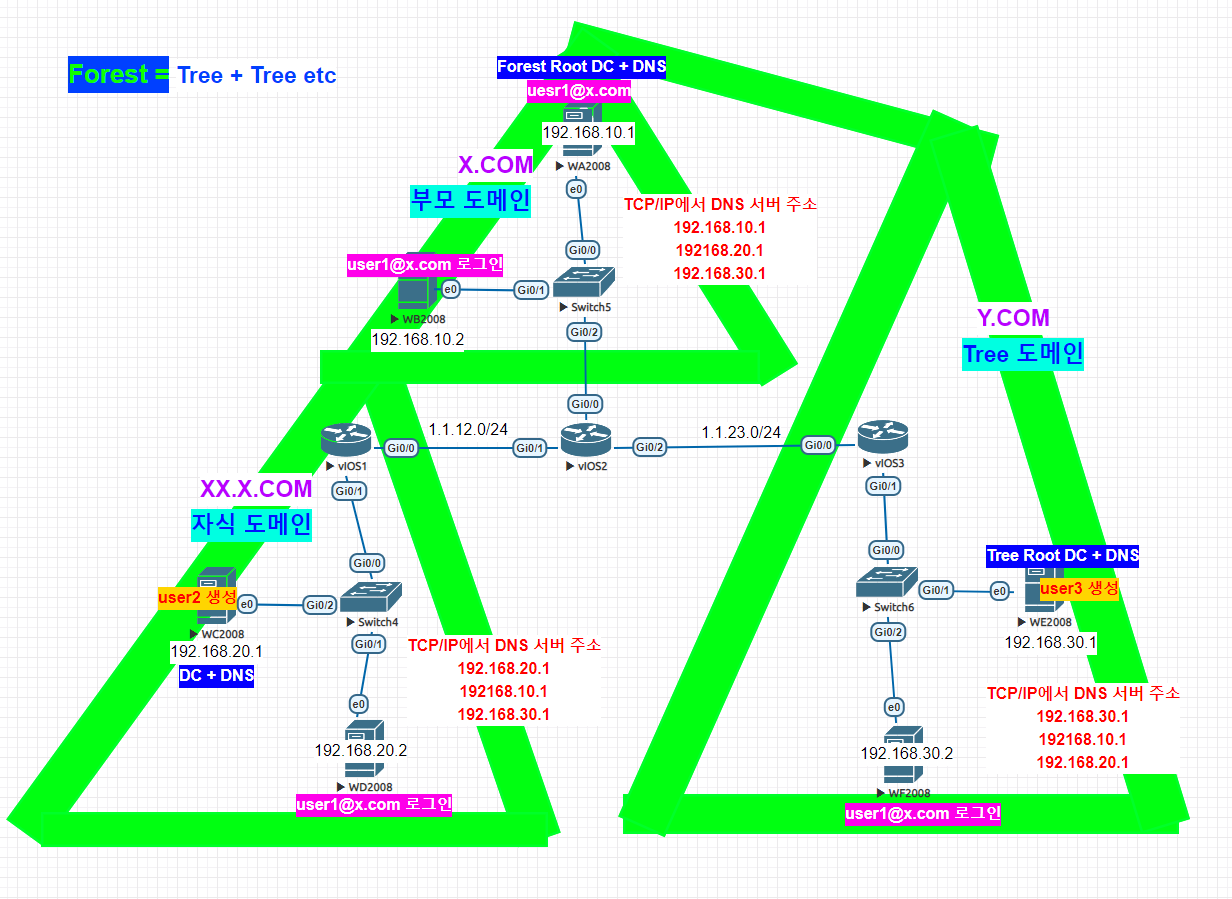
윈도우 AGDLP & AGUDLP 전략 / Trust
기본 구성
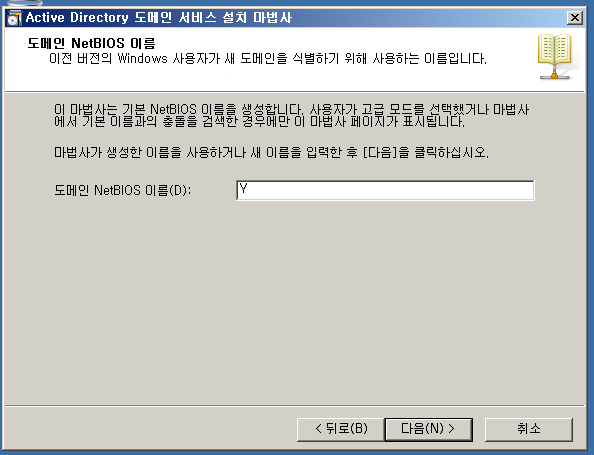
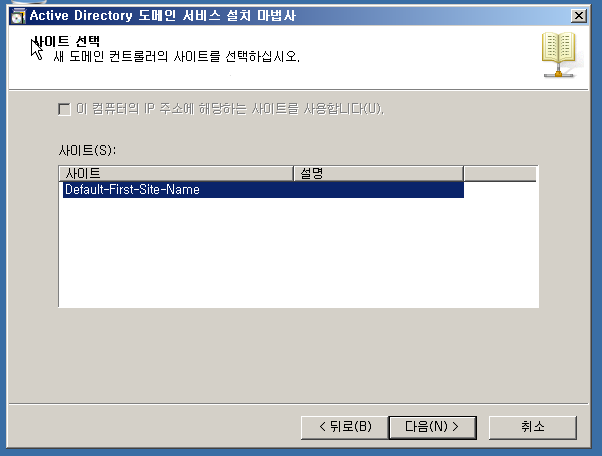
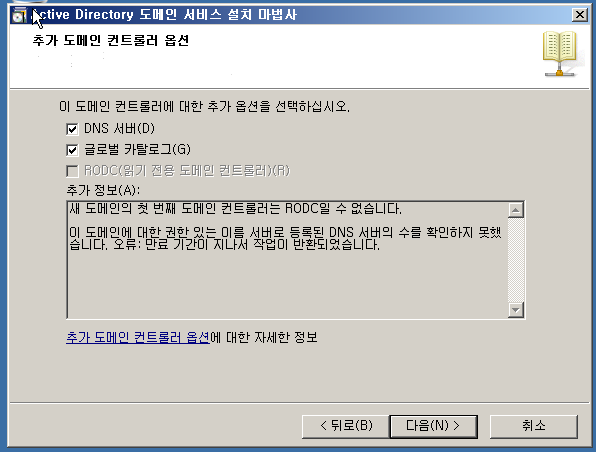
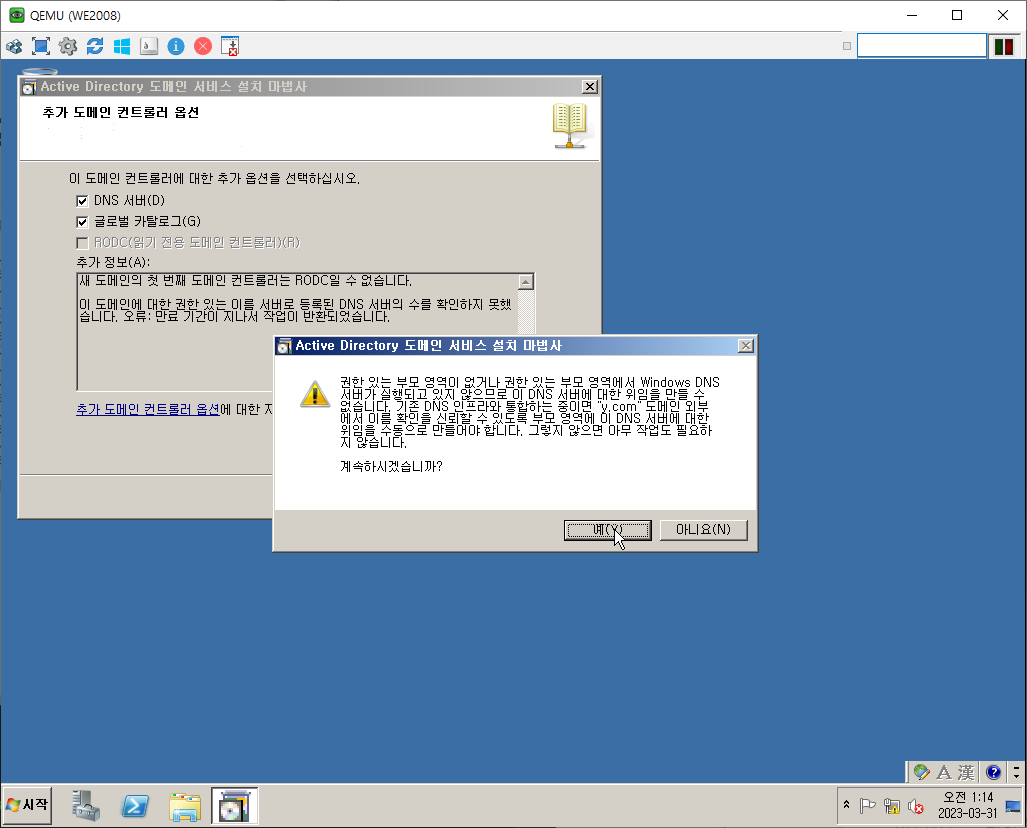
WA 설정
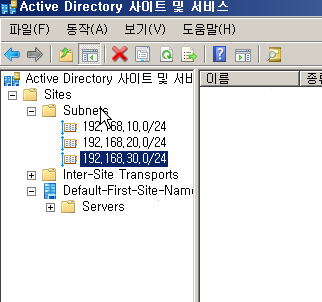
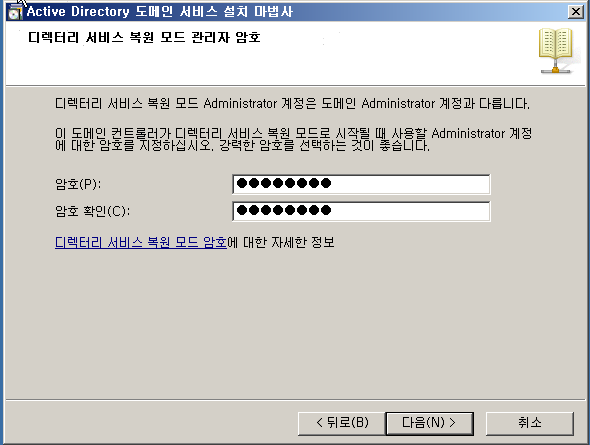
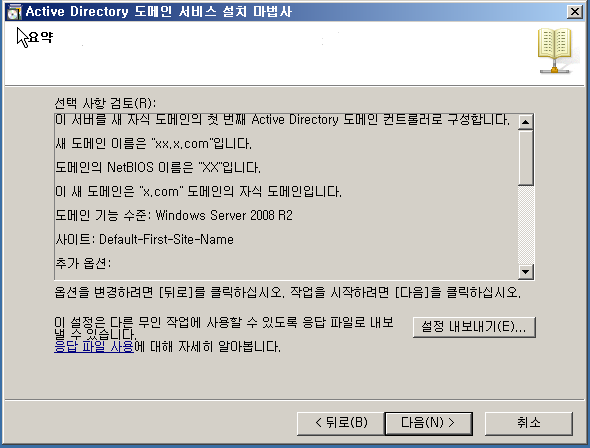
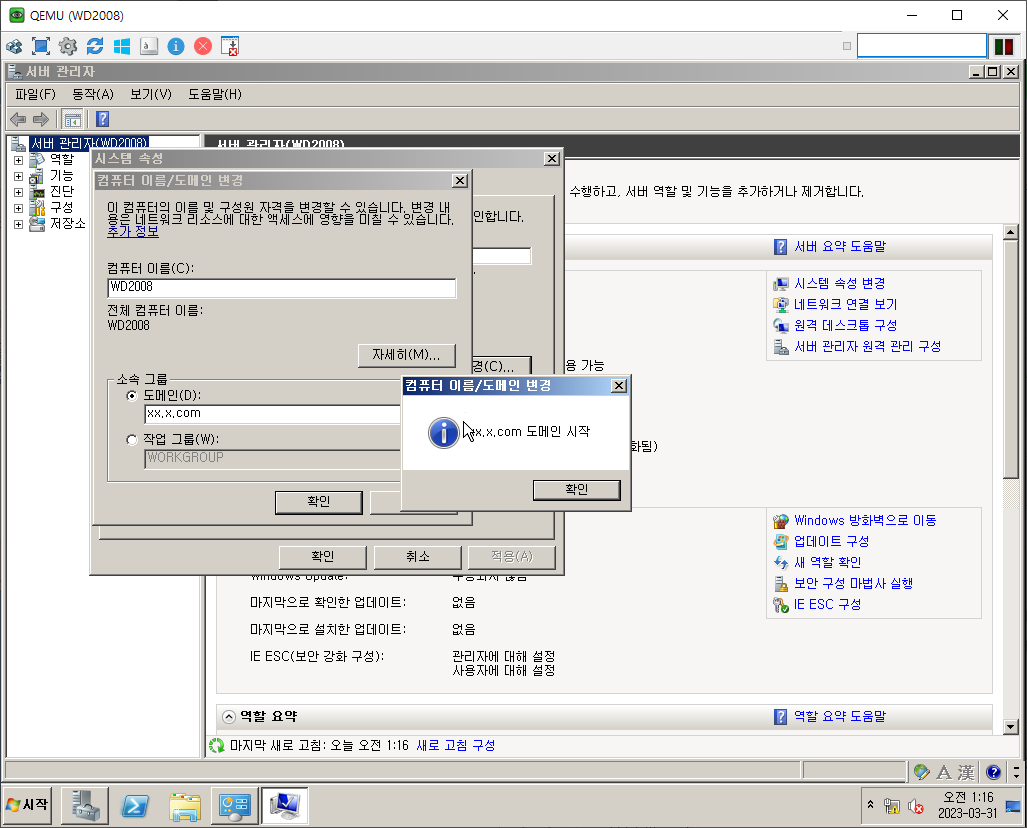
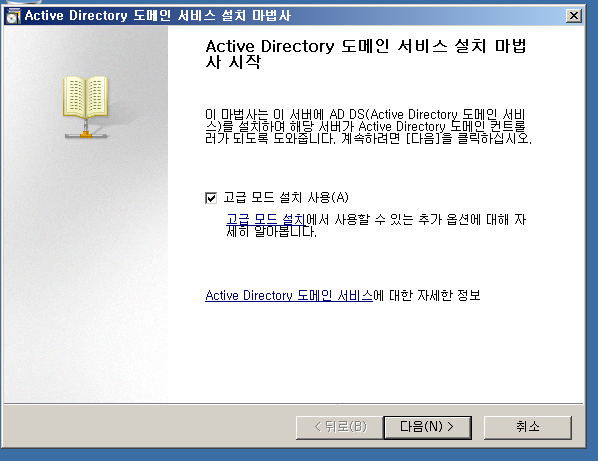
WD - DC + DNS 설치
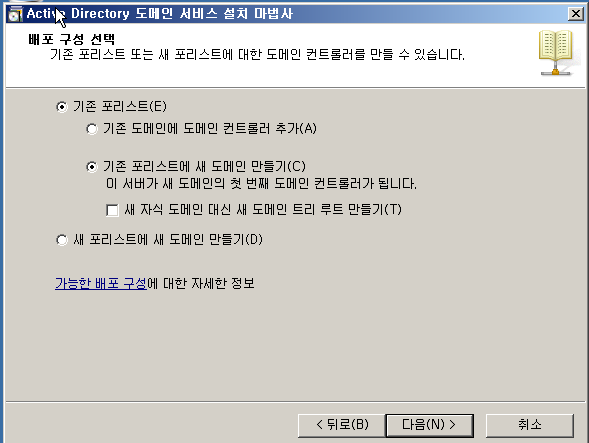 !
!
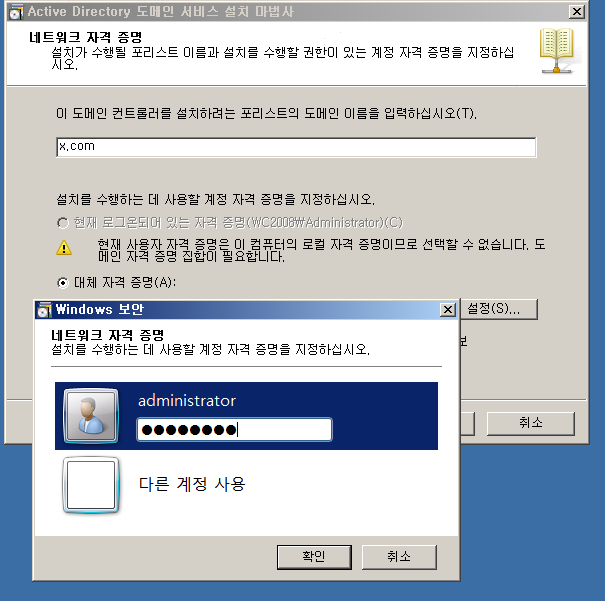
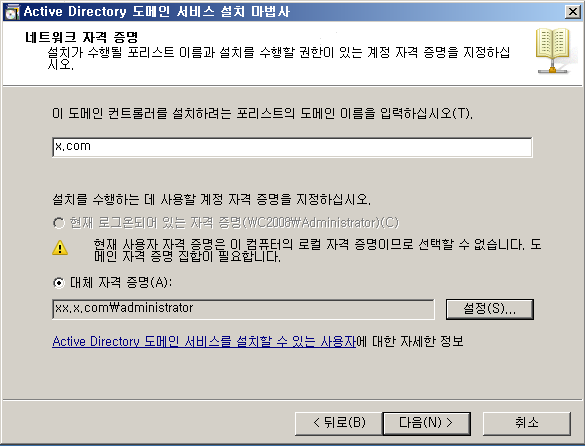
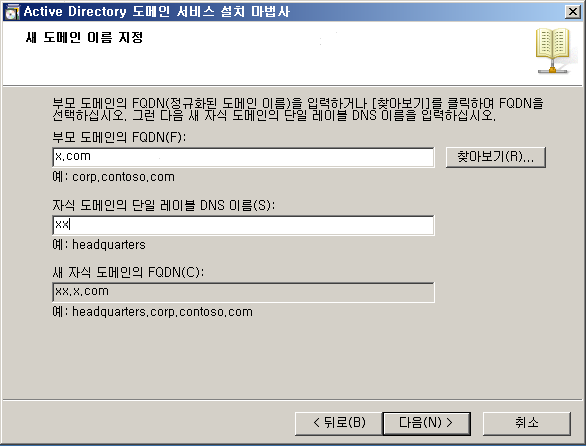
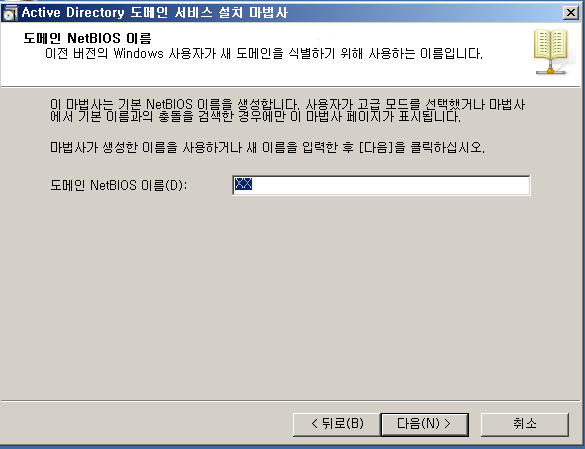
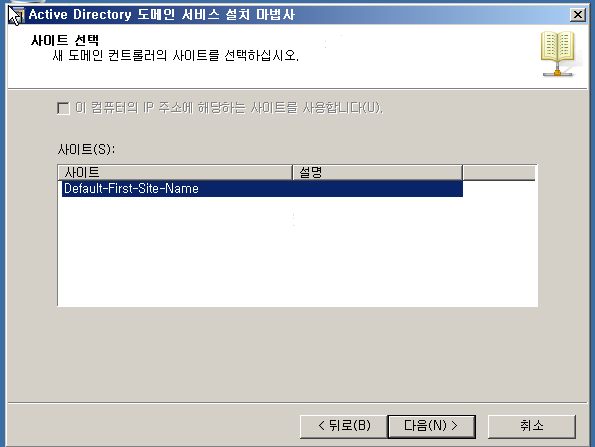
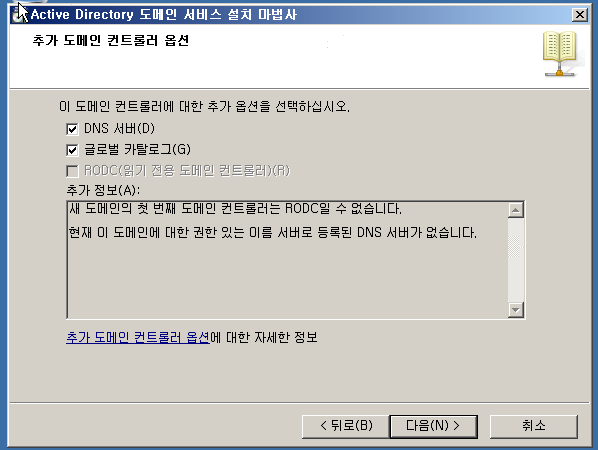
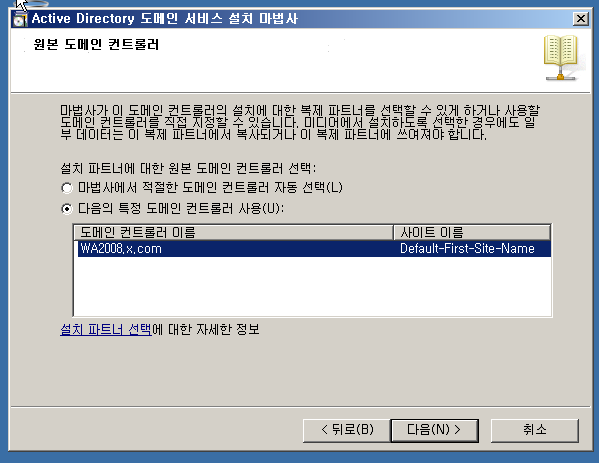
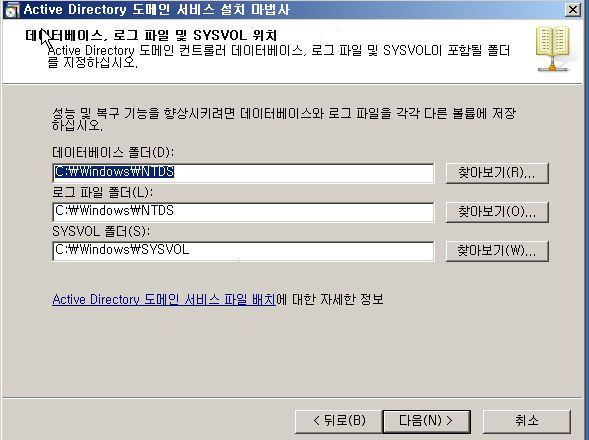
WD
WE - Tree Root DC + DNS
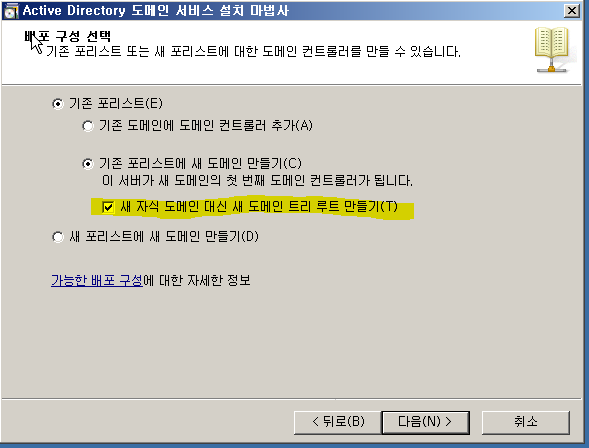
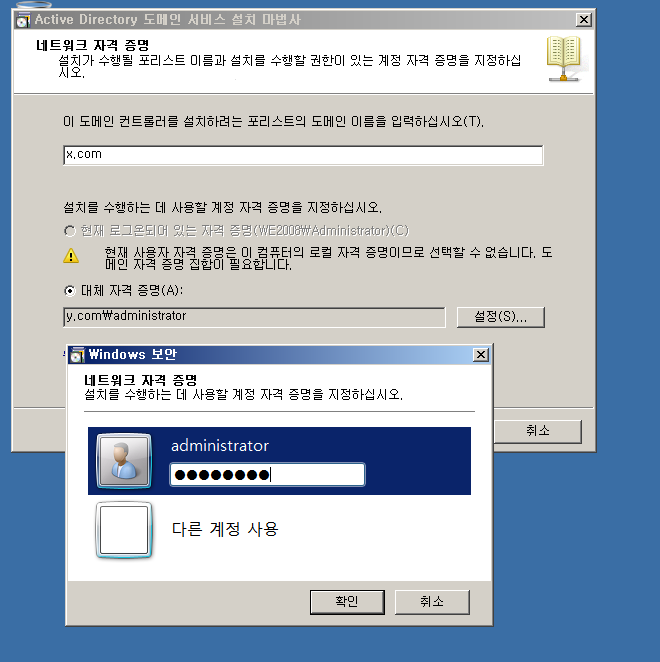
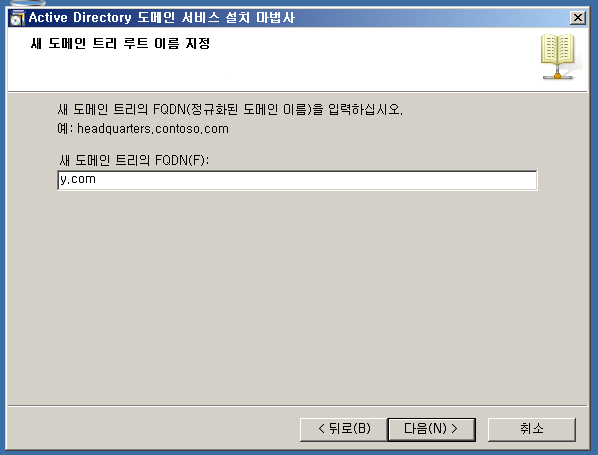
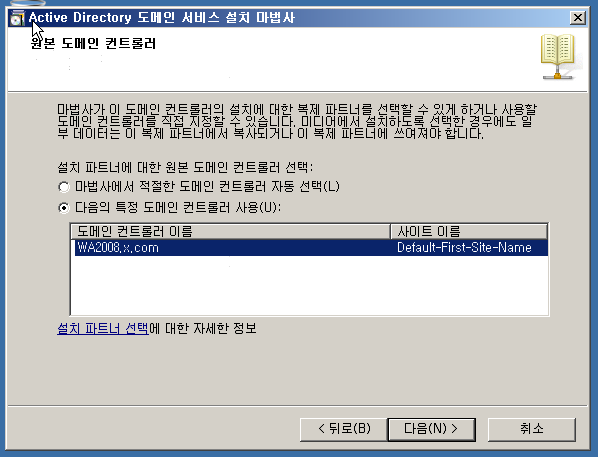
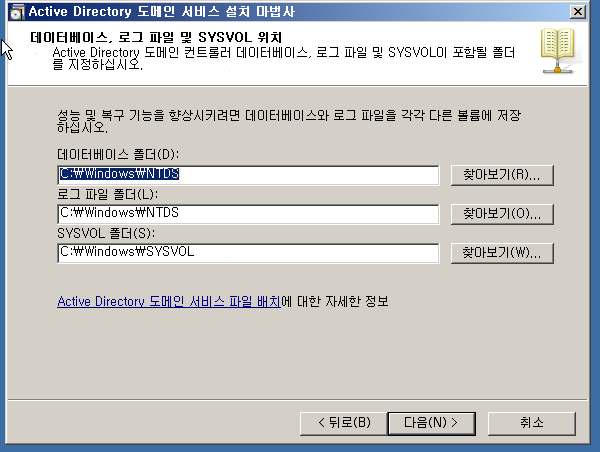
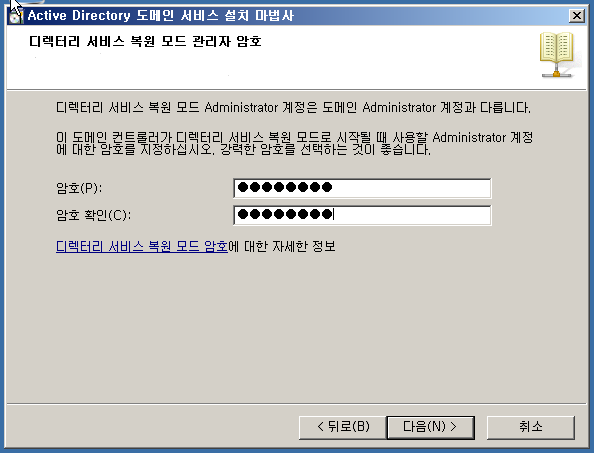
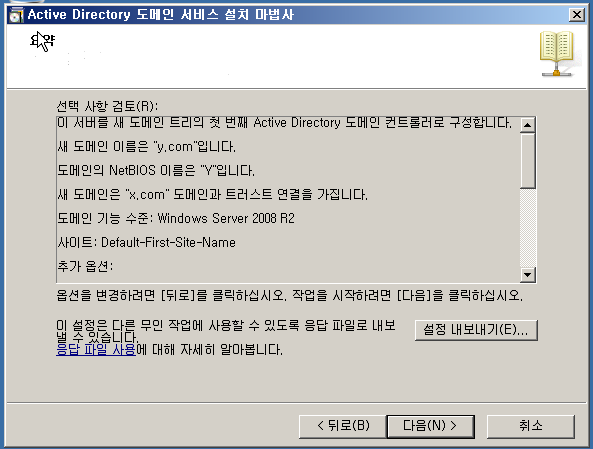
WF
계정 종류
01. A local user account
- enables a user to log on to a specific computer to access resources on that computer.
02. A domain user account
- enables a user to log on to the domain to access network resources or to log on to an individual computer to access resources on that computer.
03. A built-in user account
- enables a user to perform administrative tasks or gain temporary access to network resources.
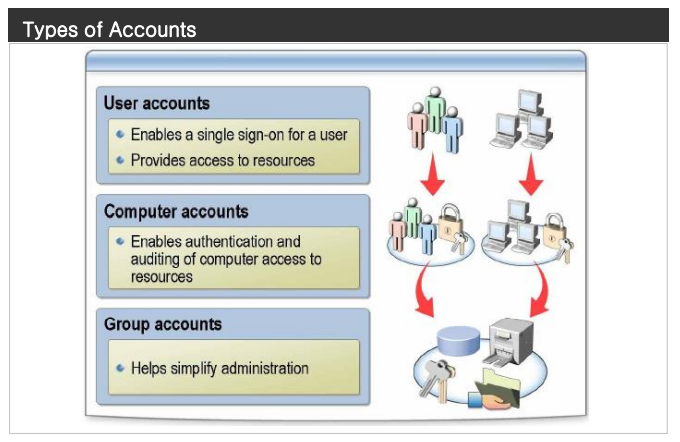
Computer accounts
- Every computer running Microsoft Windows NT®, Windows 2000, or Windows XP, or a server running Windows Server 2003 that joins a domain, has a computer account. Like user accounts, computer accounts provide a way to authenticate and audit computer access to the network and to domain resources. Each computer account must be unique.
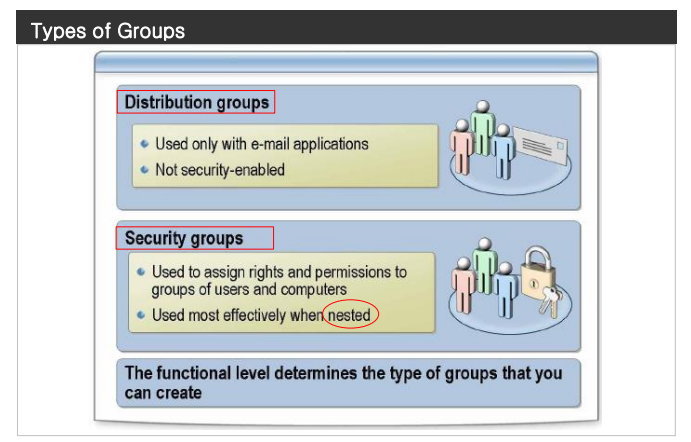
Group accounts
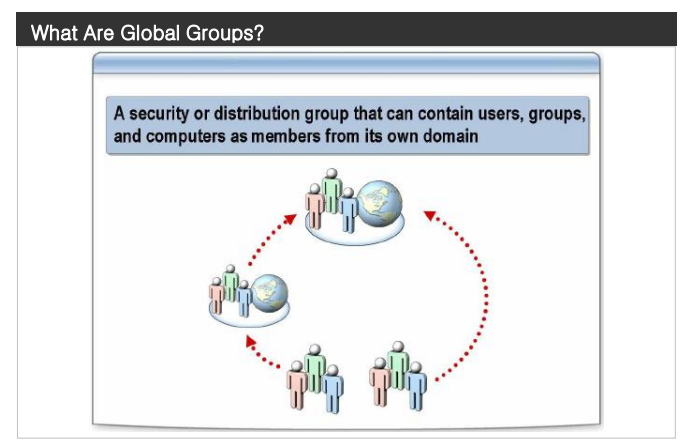
- A group account is a collection of users, computers, or other groups. You can use groups to efficiently manage access to domain resources, which helps simplify administration. When you use groups, you assign permissions for shared resources, such as folders and printers, only once.rather than multiple times.to individual users.
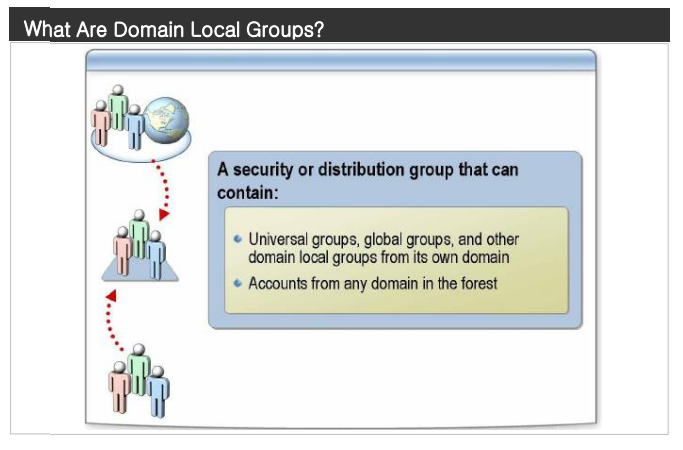
Membership. In Windows 2000 mixed mode, domain local groups can contain user accounts and global groups from any domain. In Windows 2000 native mode, domain local groups can contain user accounts, global groups, universal groups from any trusted domain, and domain local groups from the same domain.
Can be a member of. In Windows 2000 mixed mode, a domain local group cannot be a member of any group. In Windows 2000 native mode, a domain local group can be a member of domain local groups from the same domain.
Scope. A domain local group is visible only in its own domain.
Permission for. You can assign permission that applies to the domain in which the domain local group exists.
When to use domain local groups
- Use a domain local group when you want to assign access permissions to resources that are located in the same domain in which you create the domain
Membership. In Windows 2000 mixed mode, a global group can contain user accounts from the same domain. In Windows 2000 native mode and in Windows Server 2003 mode, global groups can contain user accounts and global groups from the same domain.
Can be a member of. In Windows 2000 mixed mode, a global group can be a member of domain local groups in any trusted domain. In Windows 2000 native mode and in Windows Server 2003 mode, a global group can be a member of universal and domain local groups in any domain and can also be a member of global groups in the same domain.
Scope. A global group is visible in its domain and all trusted domains, which include all of the domains in the forest.
Permissions. You can assign permission to a global group that applies to all trusted domains
When to use global groups
- Because global groups are visible throughout the forest, do not create them for the purpose of allowing users access to domain-specific resources. Use global groups to organize users or groups of users. A domain local group is more appropriate to control user access to resources within a single domain.
Membership. You cannot create universal security groups in Windows 2000 mixed mode. In both Windows 2000 native mode and Windows Server 2003 mode, universal groups can contain user accounts, global groups, and other universal groups from any domain in the forest.
Can be a member of. The universal group is not applicable in Windows 2000 mixed mode. In Windows 2000 native mode, the universal group can be a member of domain local and universal groups from any domain.
Scope. Universal groups are visible in all domains in the forest.
Permissions. You can assign permission to a universal group that applies to all domains in the forest.
When to use universal groups
- Use universal groups when you want to nest global groups. This way, you can assign permissions to related resources in multiple domains. A Windows Server 2003 domain must be in Windows 2000 native mode or Windows Server 2003 mode to use universal security groups. You can use universal distribution groups in a Windows Server 2003 domain that is in Windows 2000 mixed mode or higher.
WA
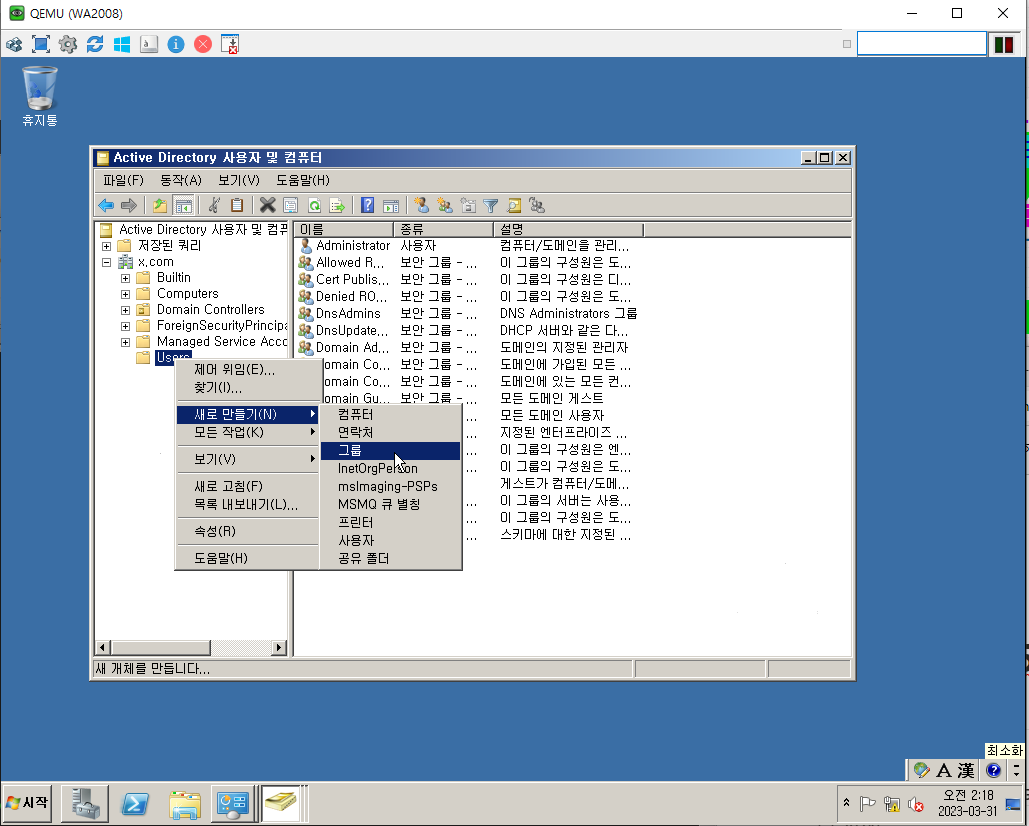
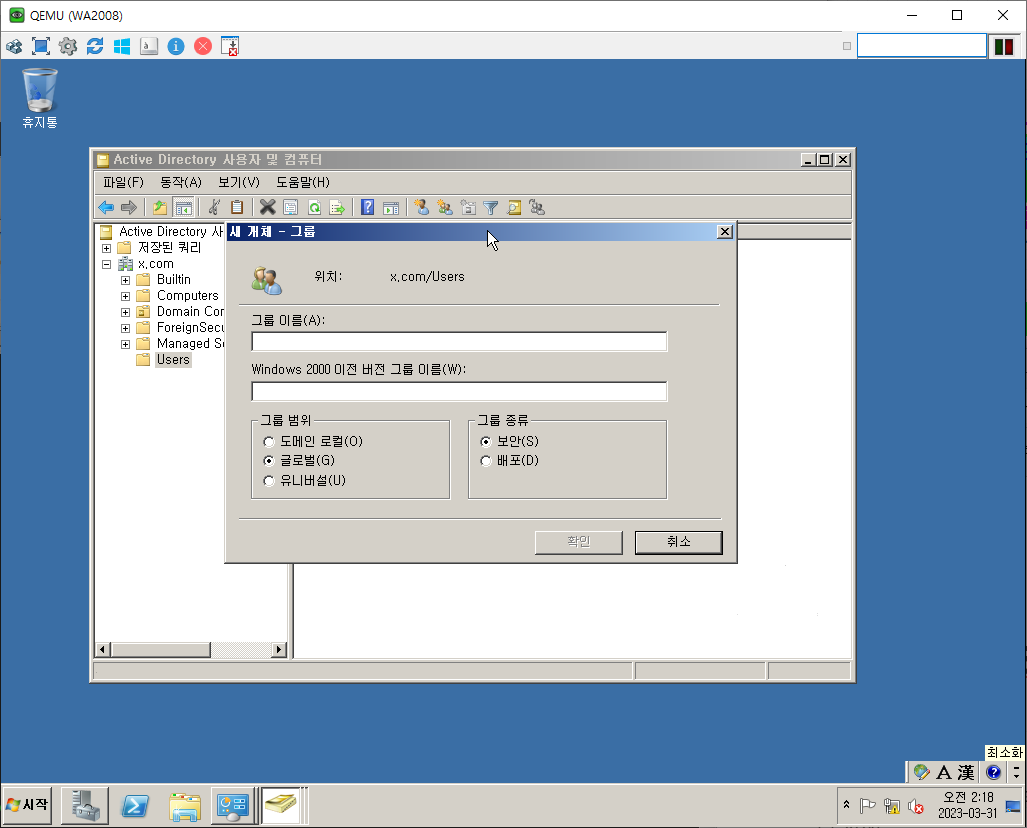
Ex.
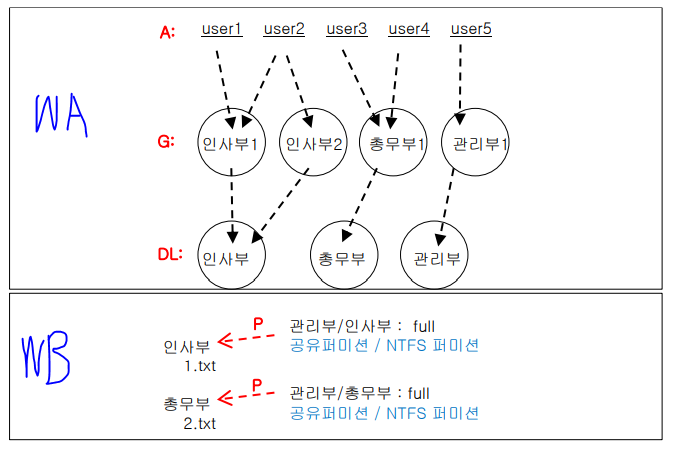
AGUDLP 전략
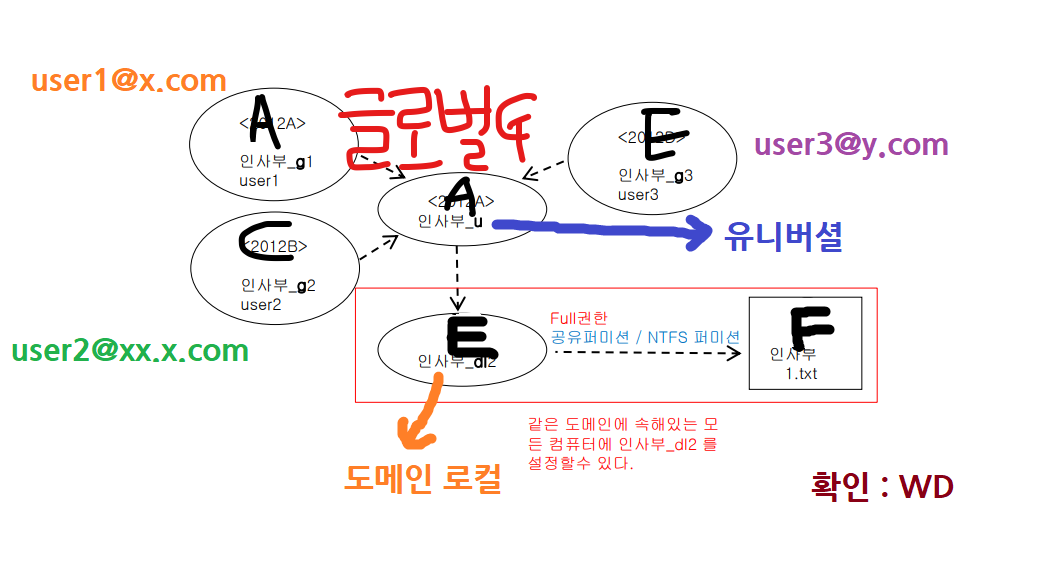
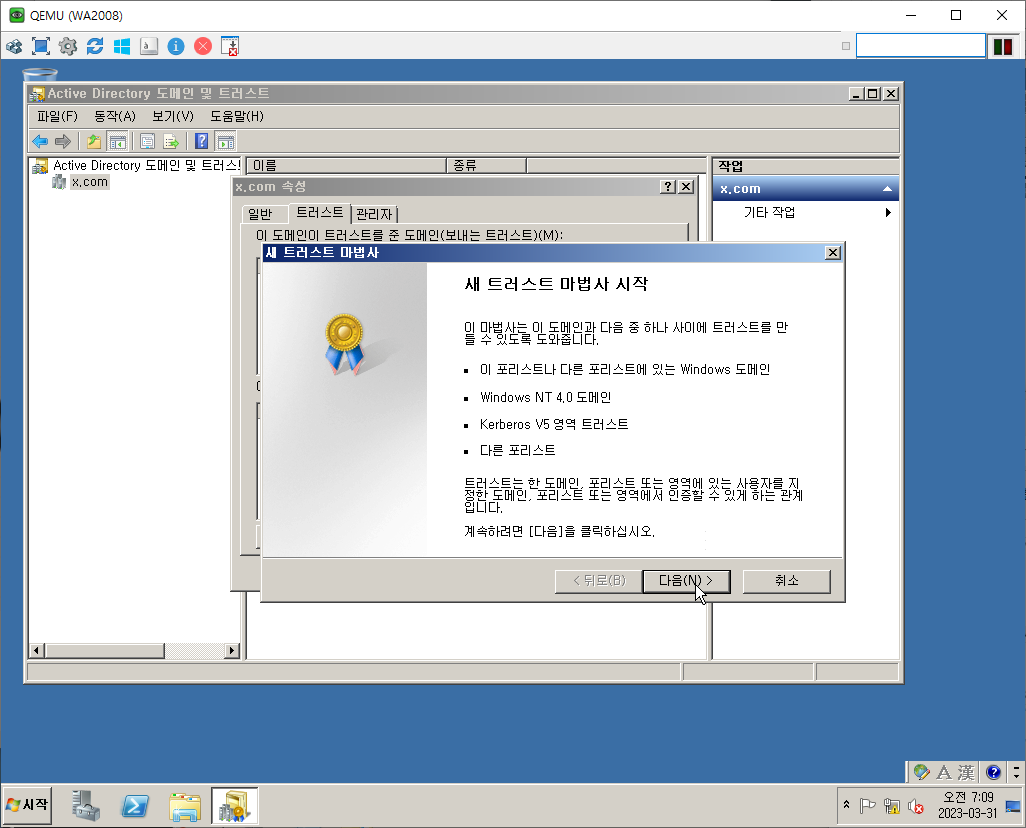
Trust

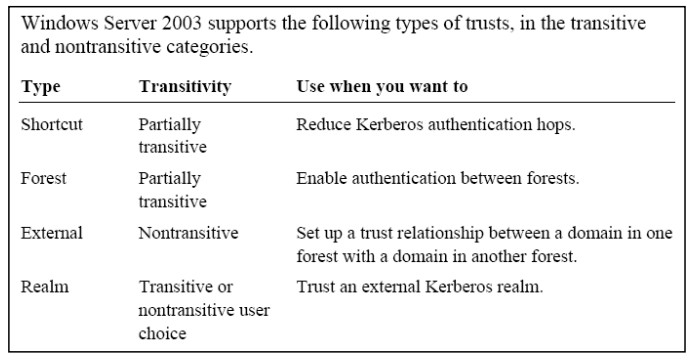
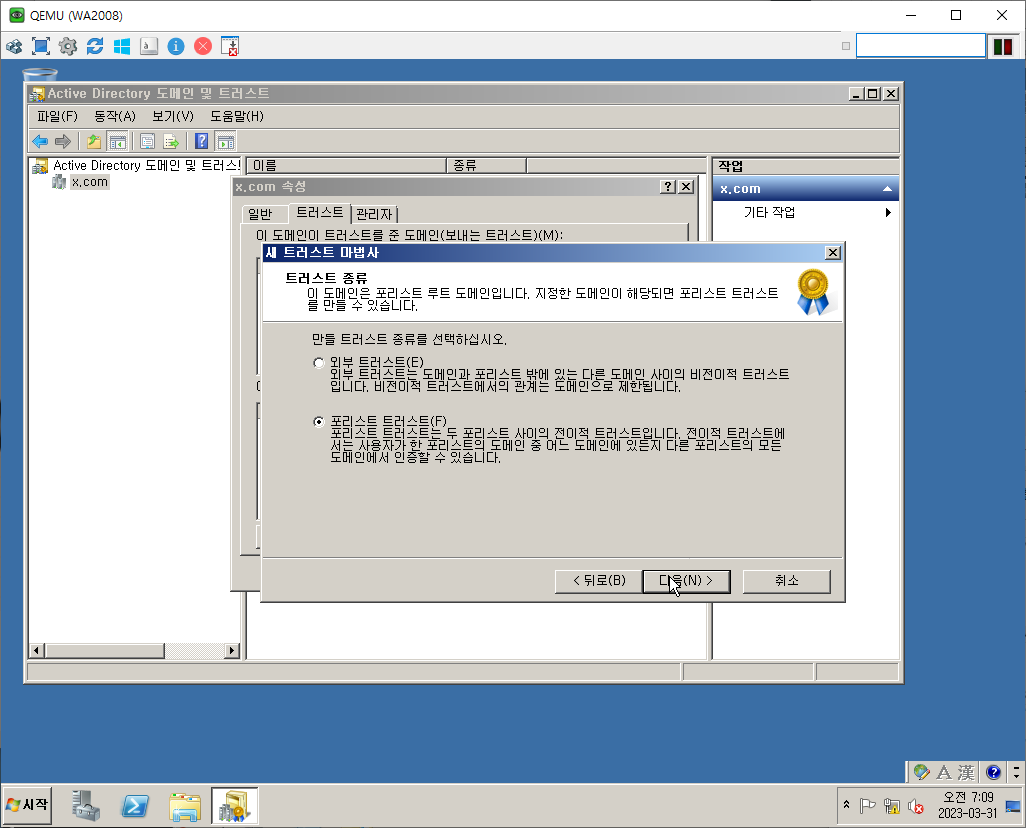
Transitive vs. nontransitive trusts
domain D directly trusts domain E, which directly trusts domain F. Because both trusts are transitive, domain D indirectly trusts domain F and vice versa. Transitive trusts are automatic. An example of transitive trust is a parent/child trust.
Nontransitive trusts are not automatic and must be set up. the trust between a domain in one forest and a domain in another forest.
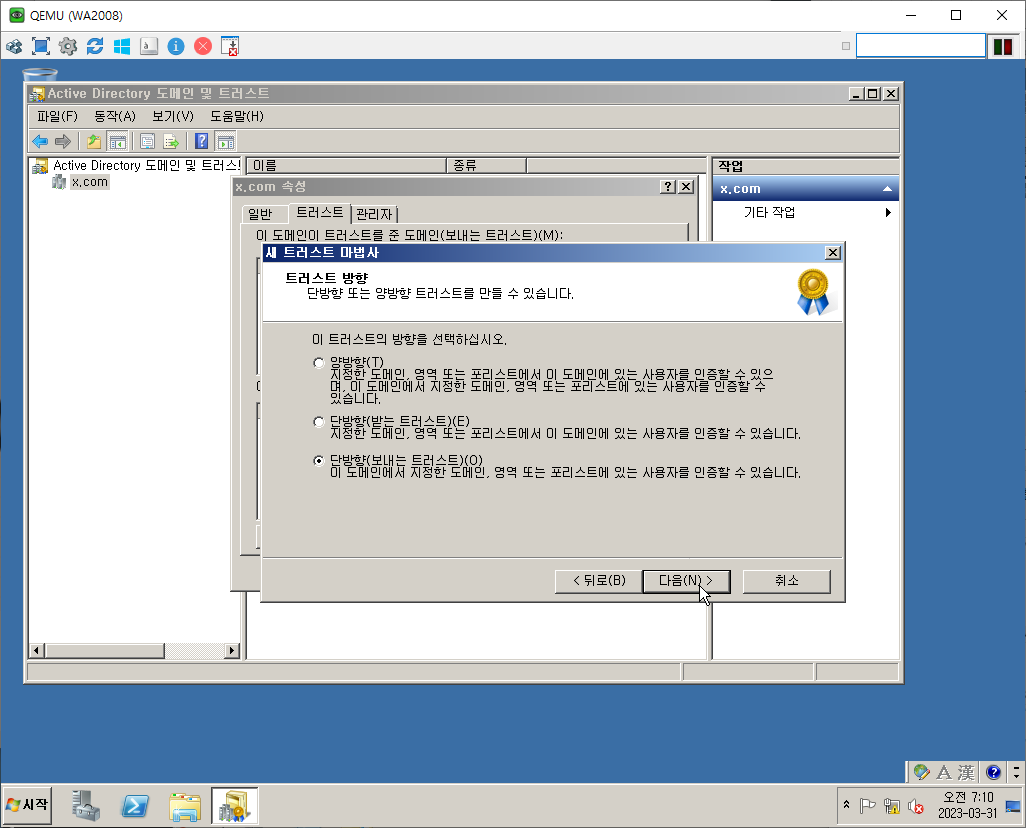
Trust direction
If in domain B, you set up a one-way incoming trust between domain B and domain Q, users in domain B can be authenticated in domain Q.
If you set up a one-way outgoing trust between domain B and domain Q, users in domain Q can be authenticated in domain B.
WA
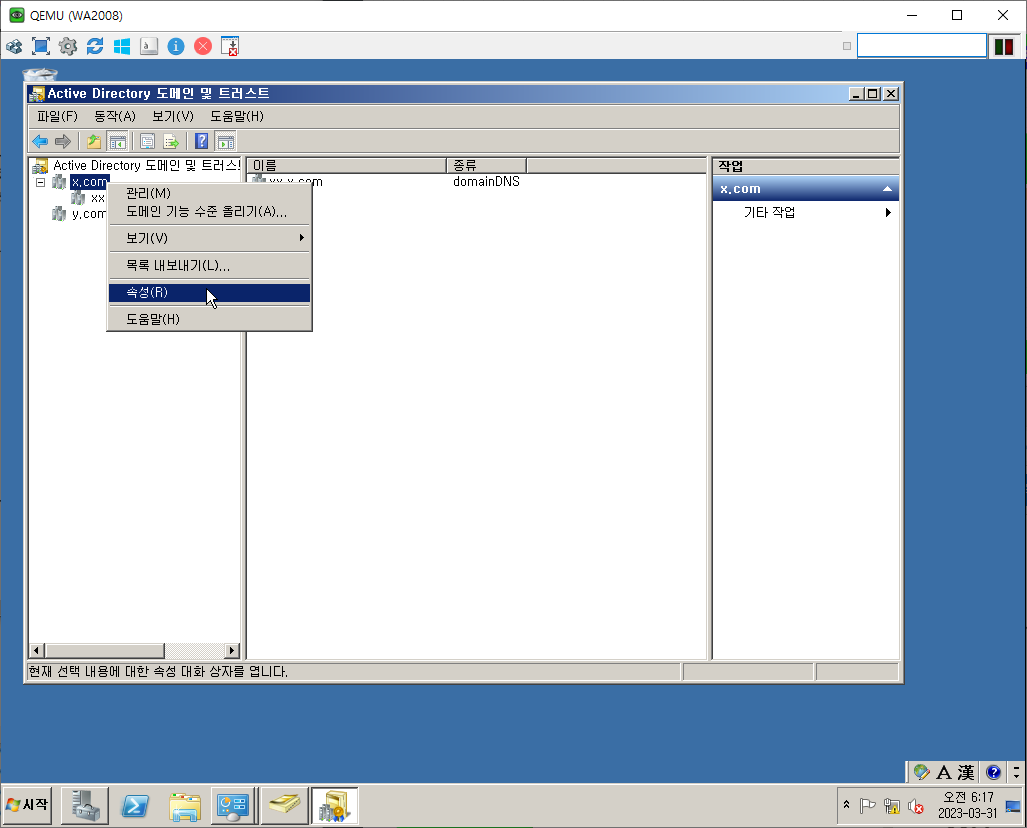

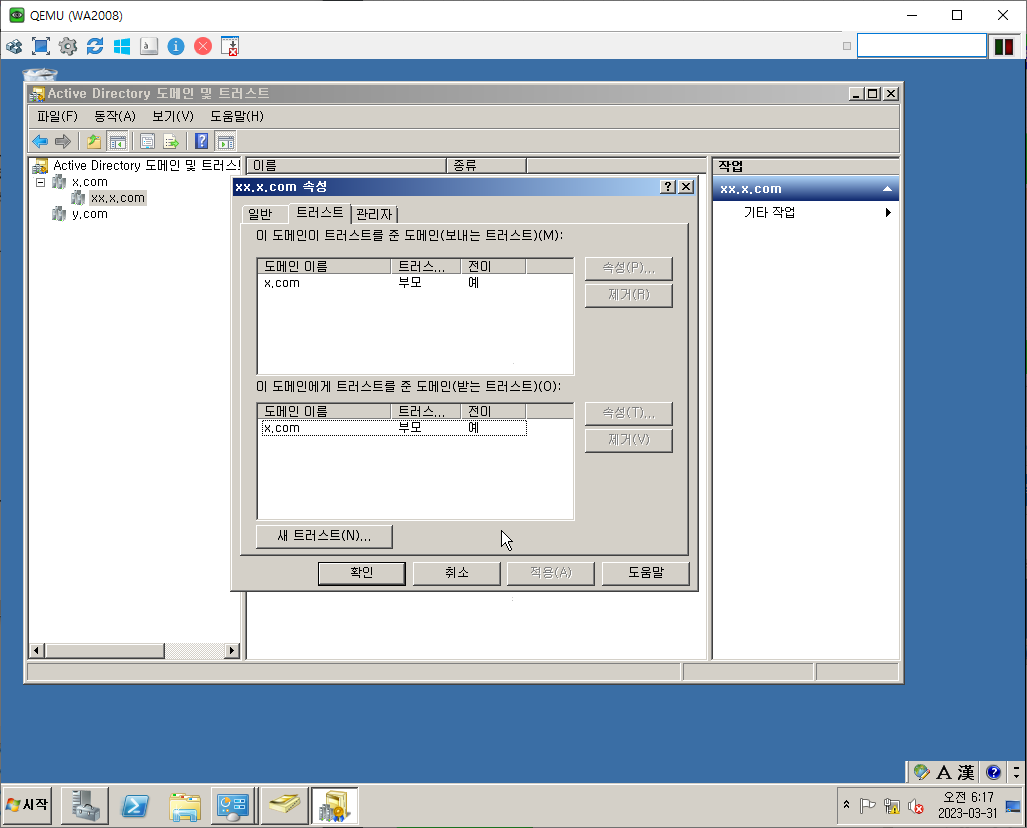
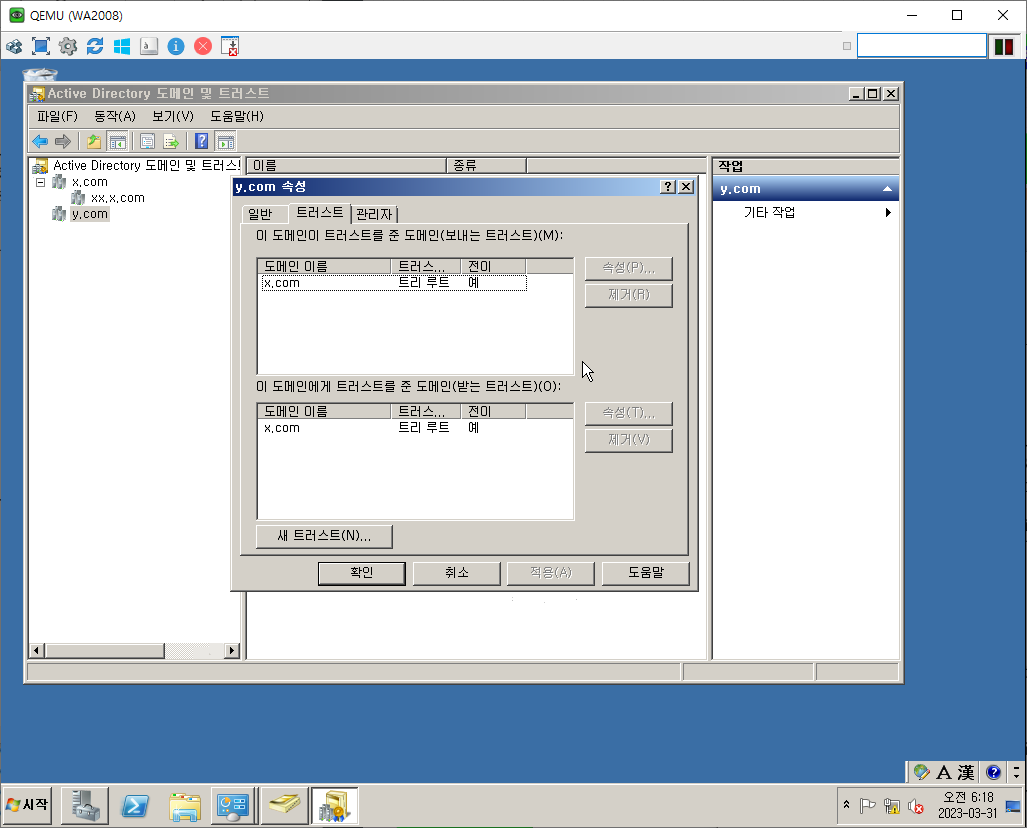
Trust Ex.

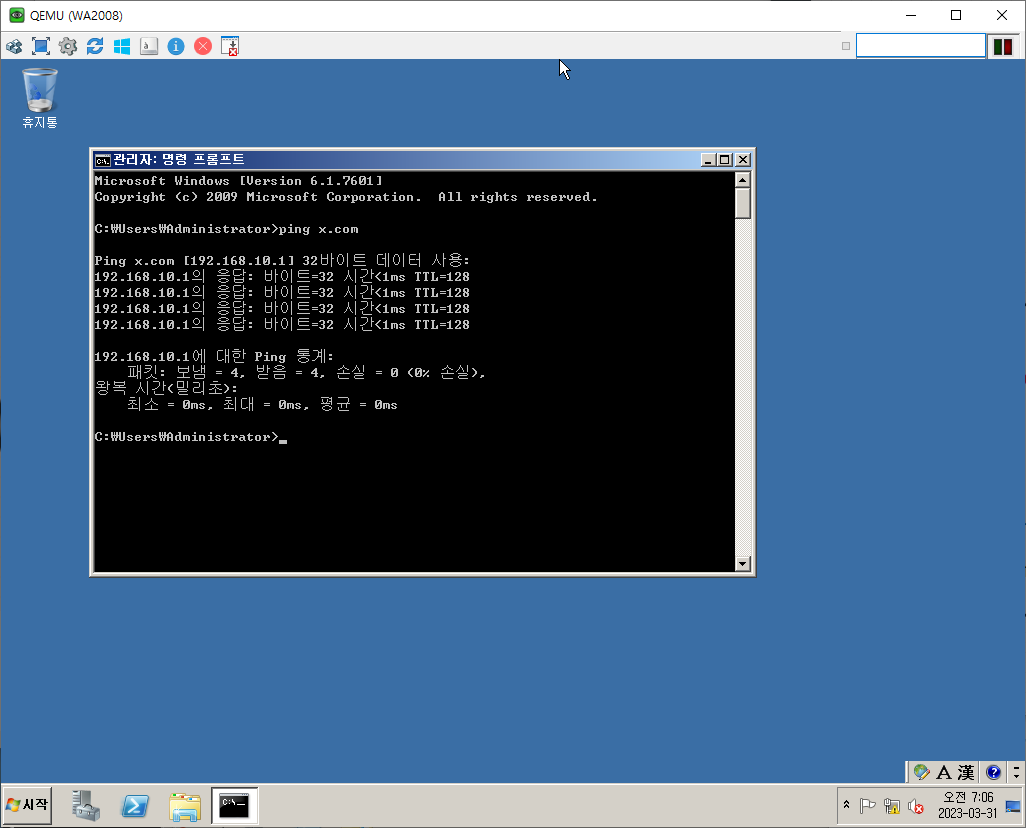
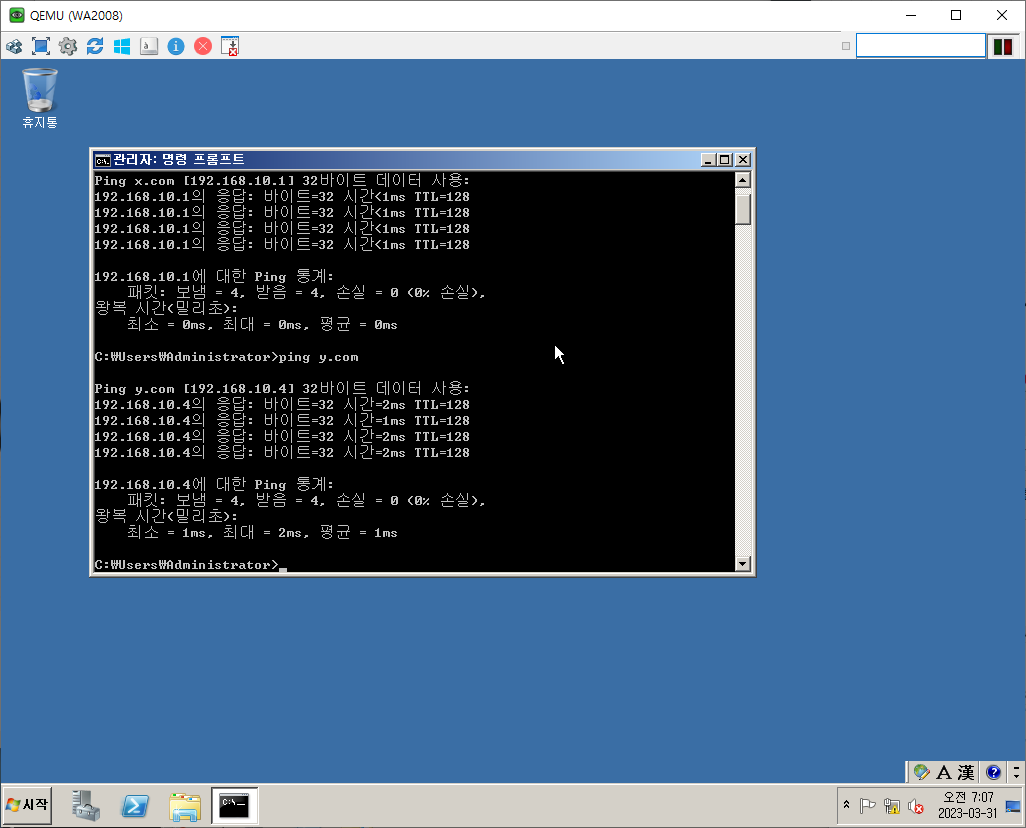
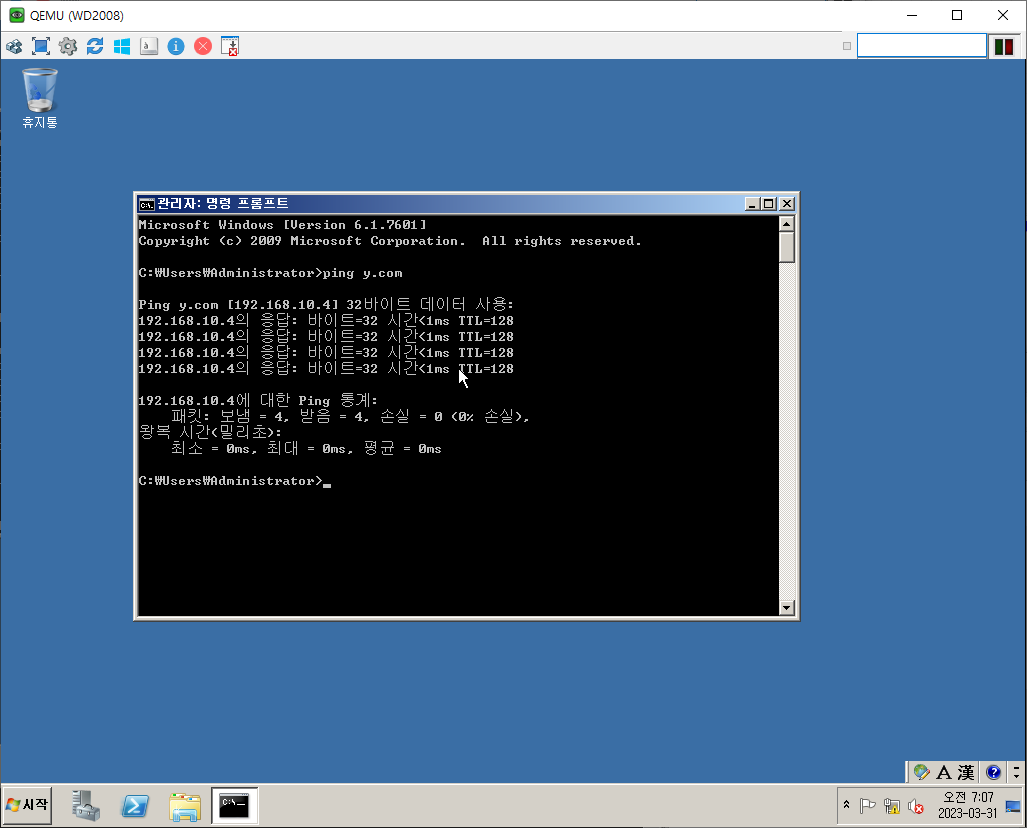
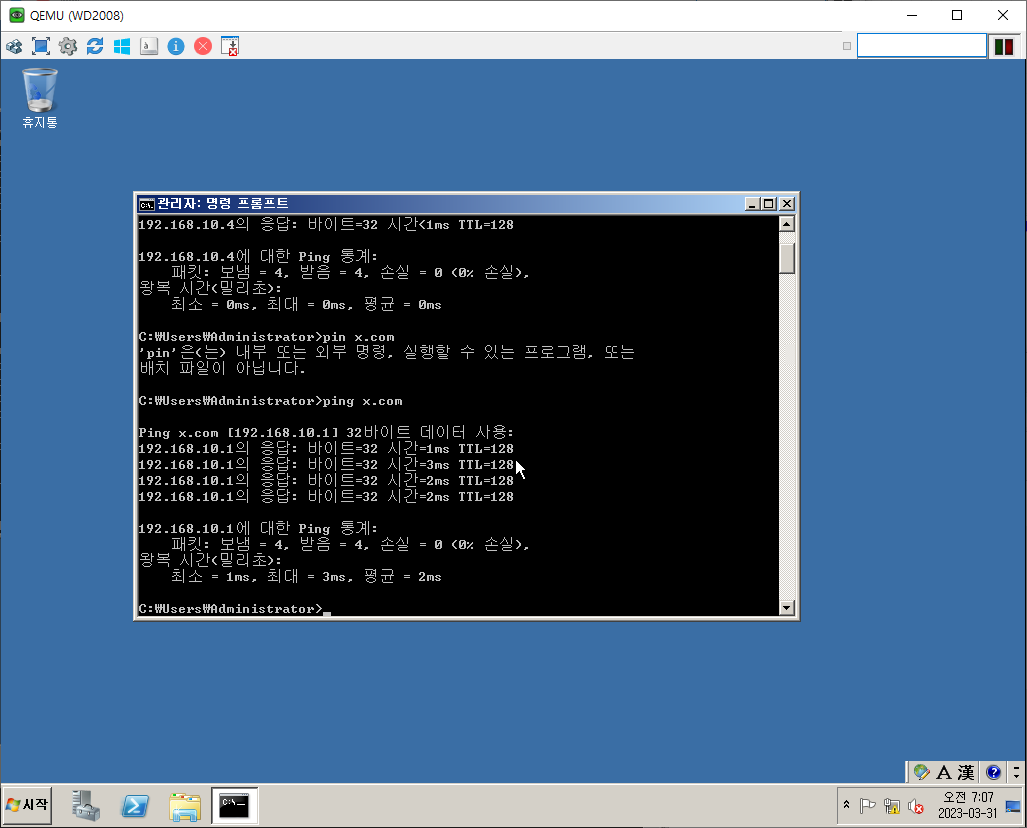
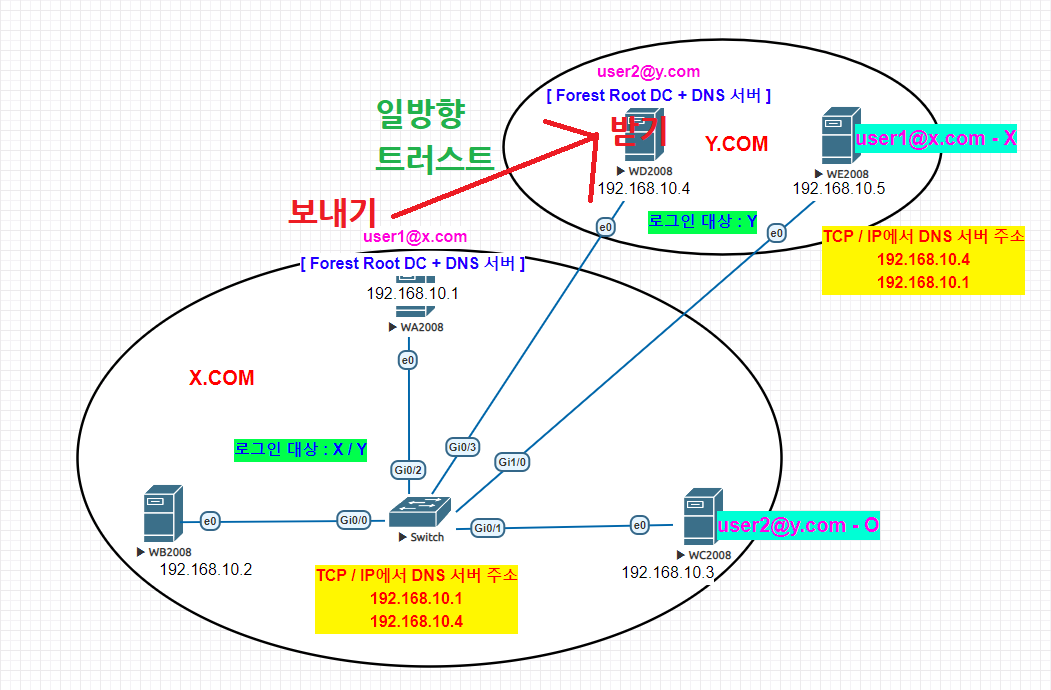
단방향 Trust
WA
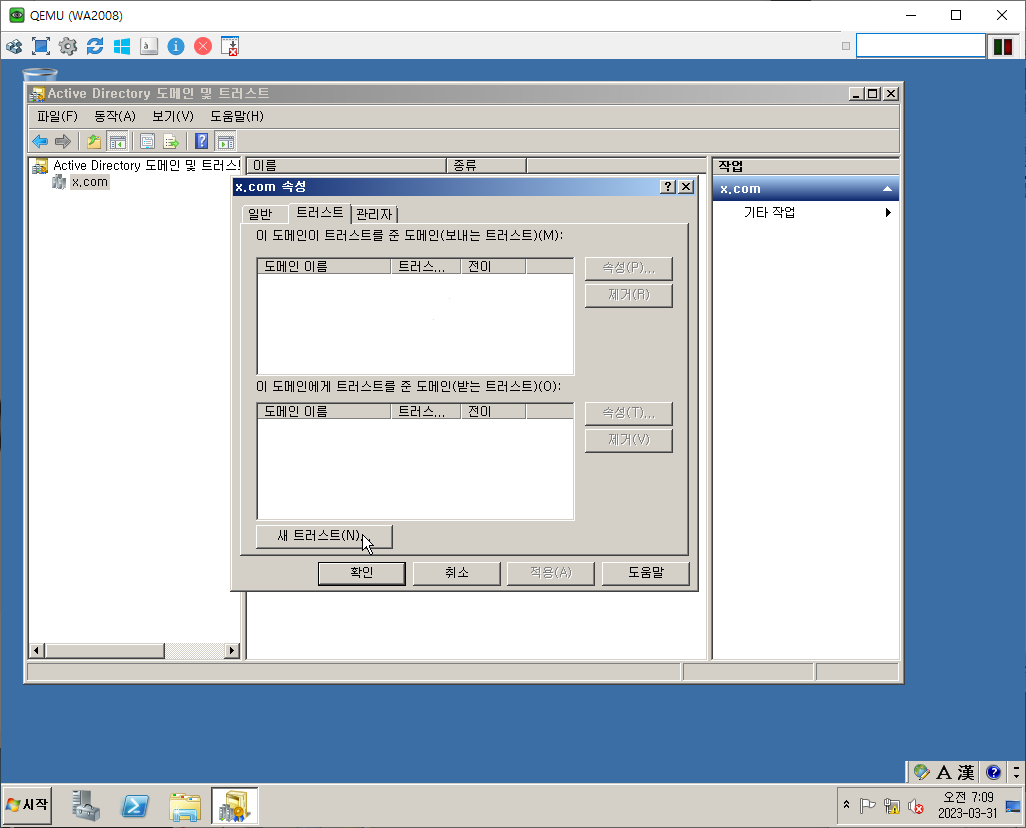
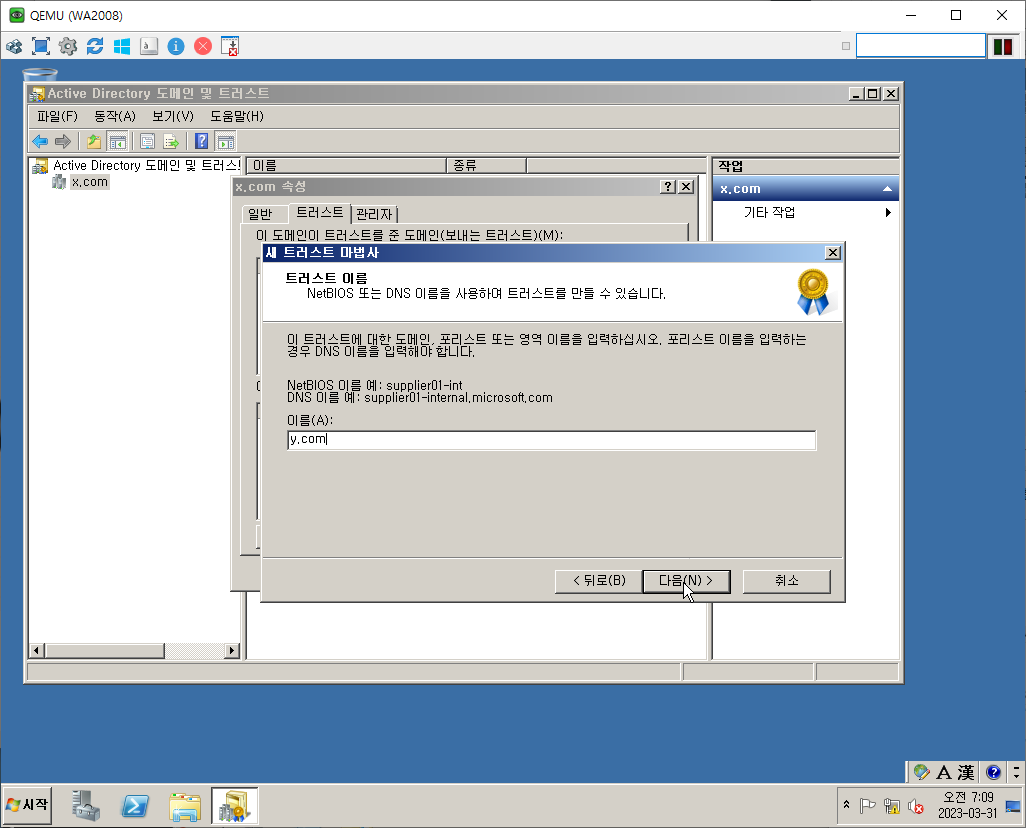
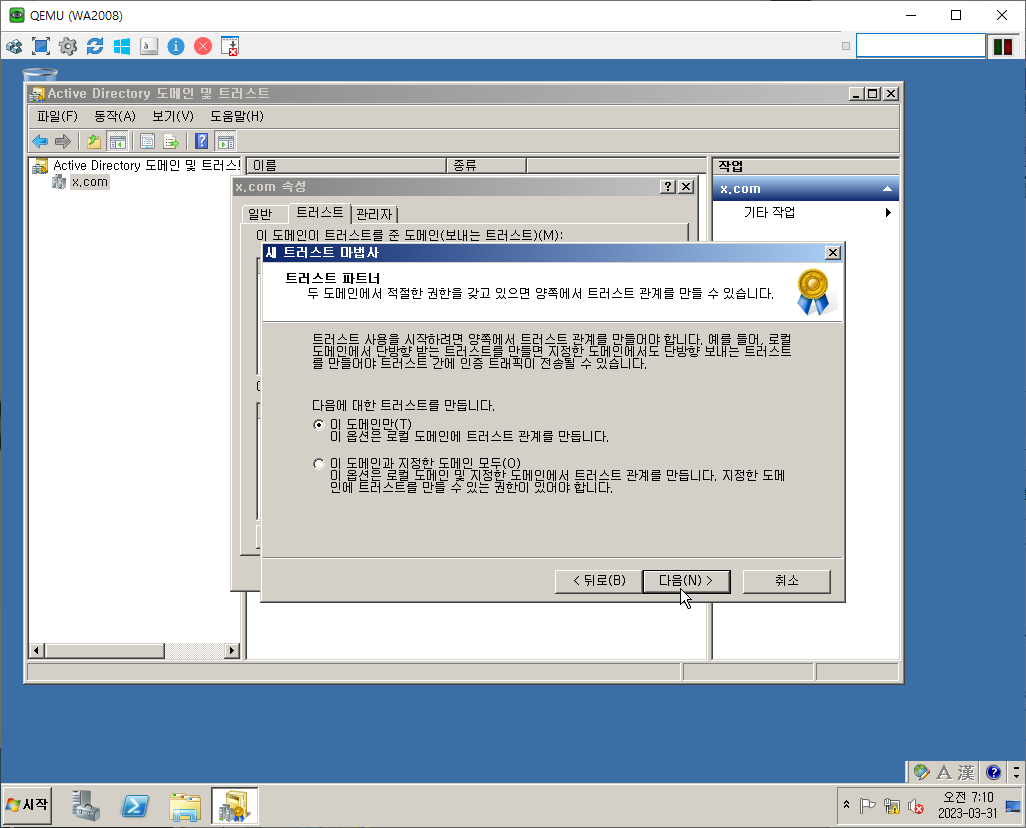
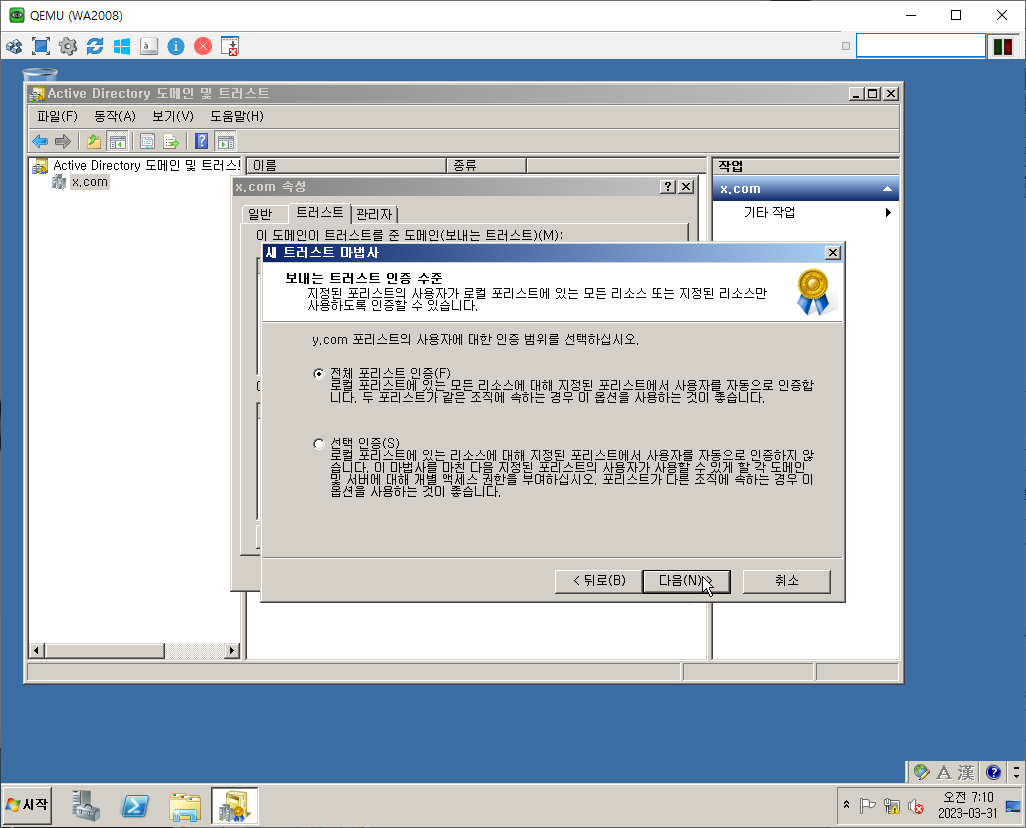
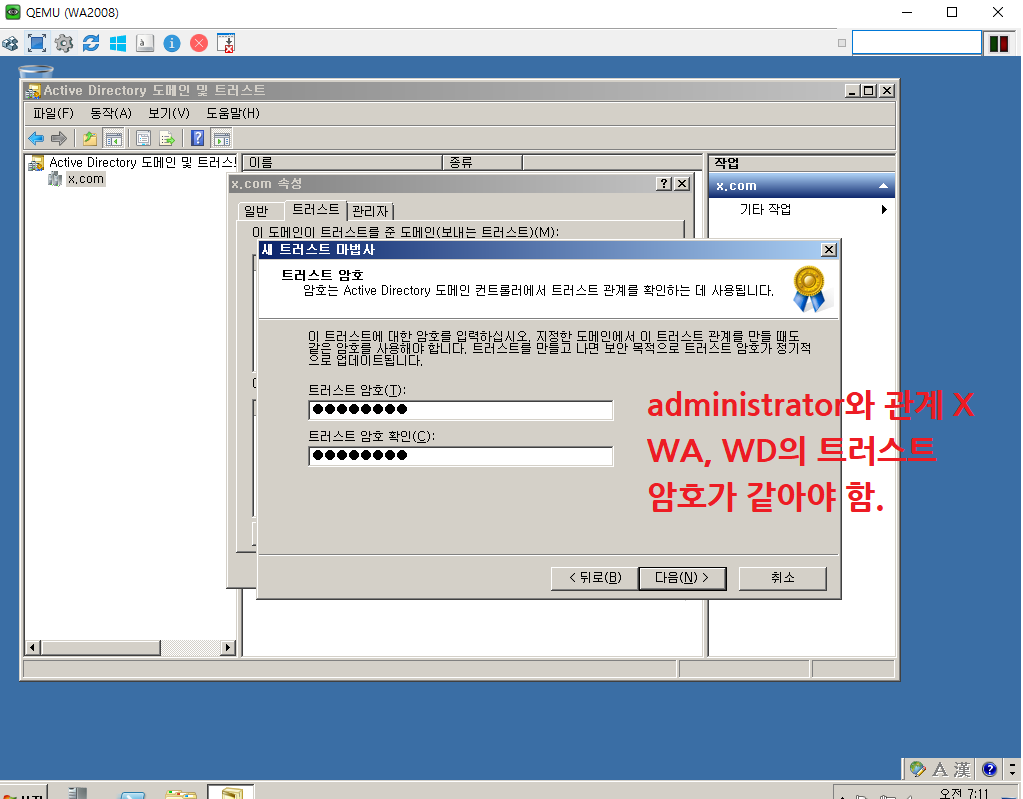
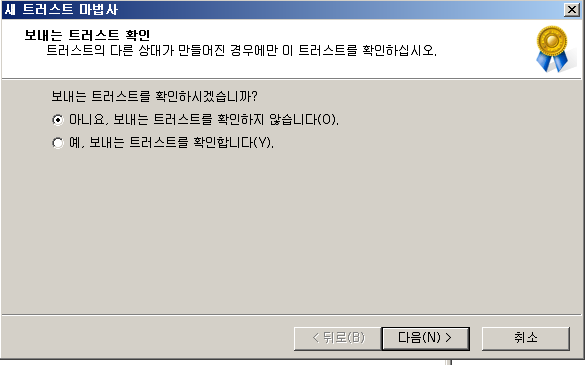
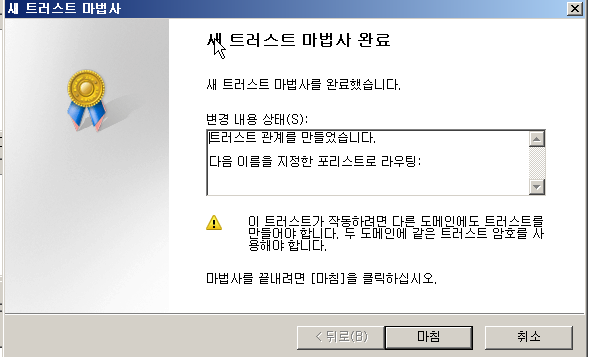
WD
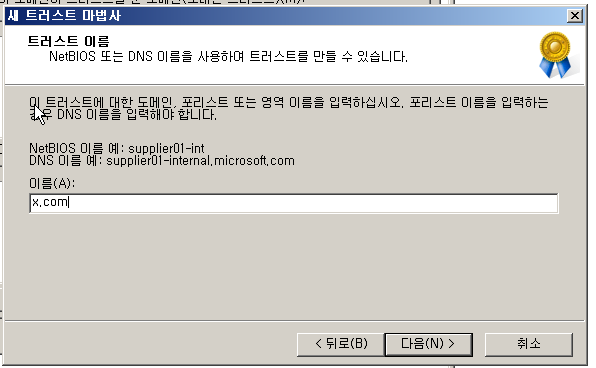
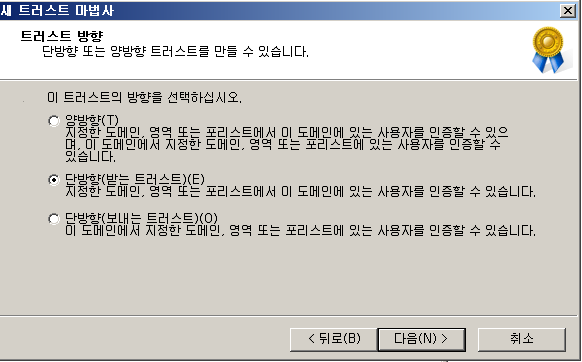
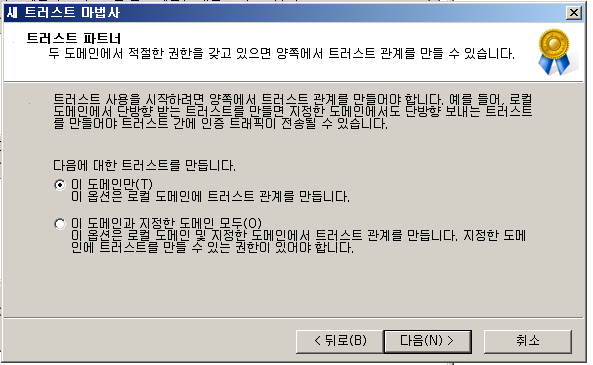
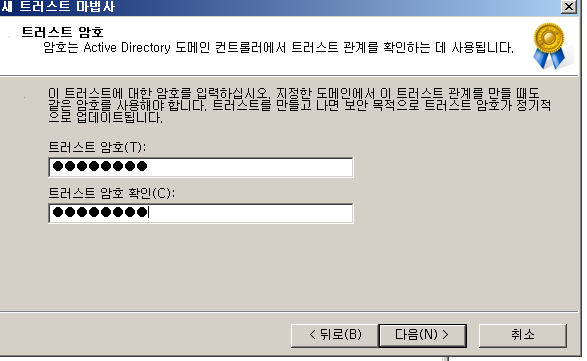
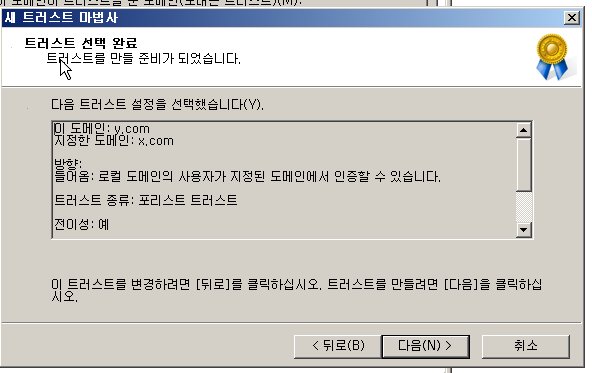
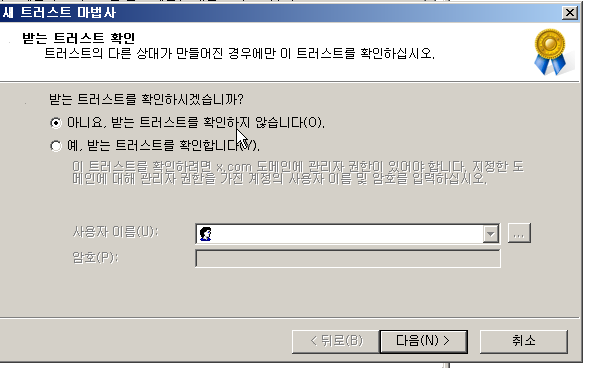
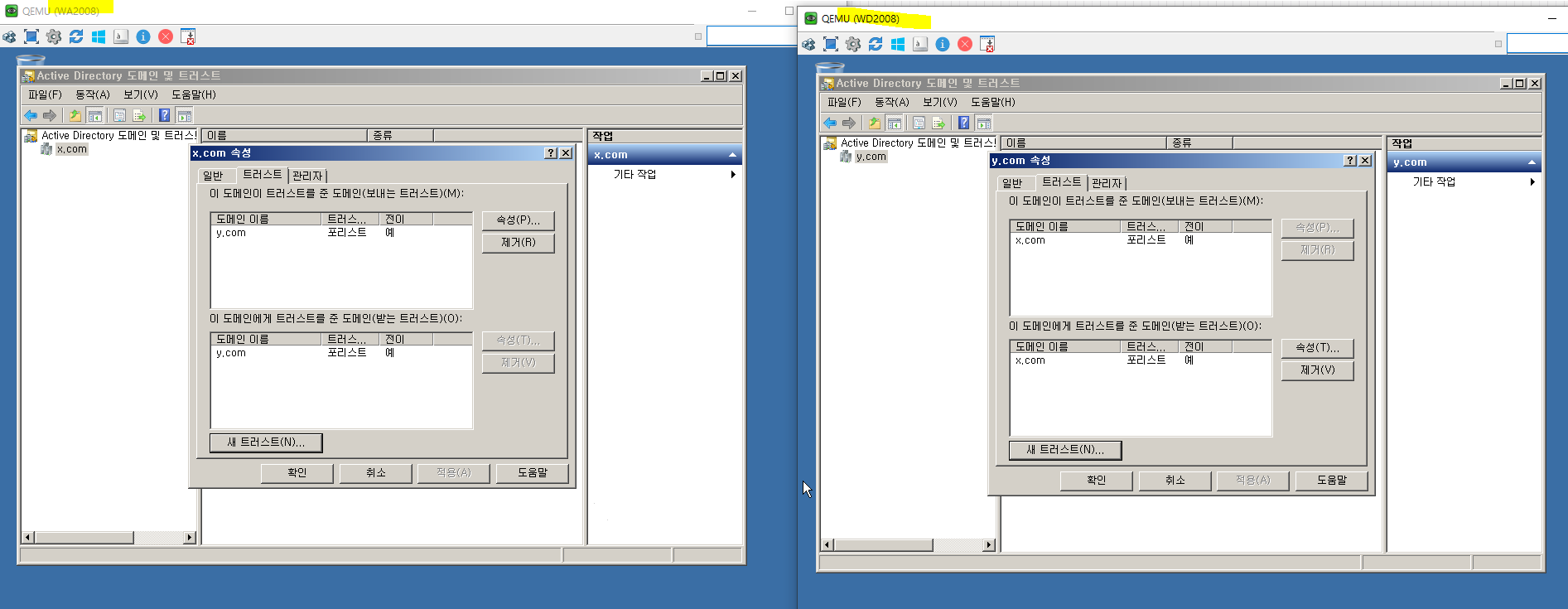
결과
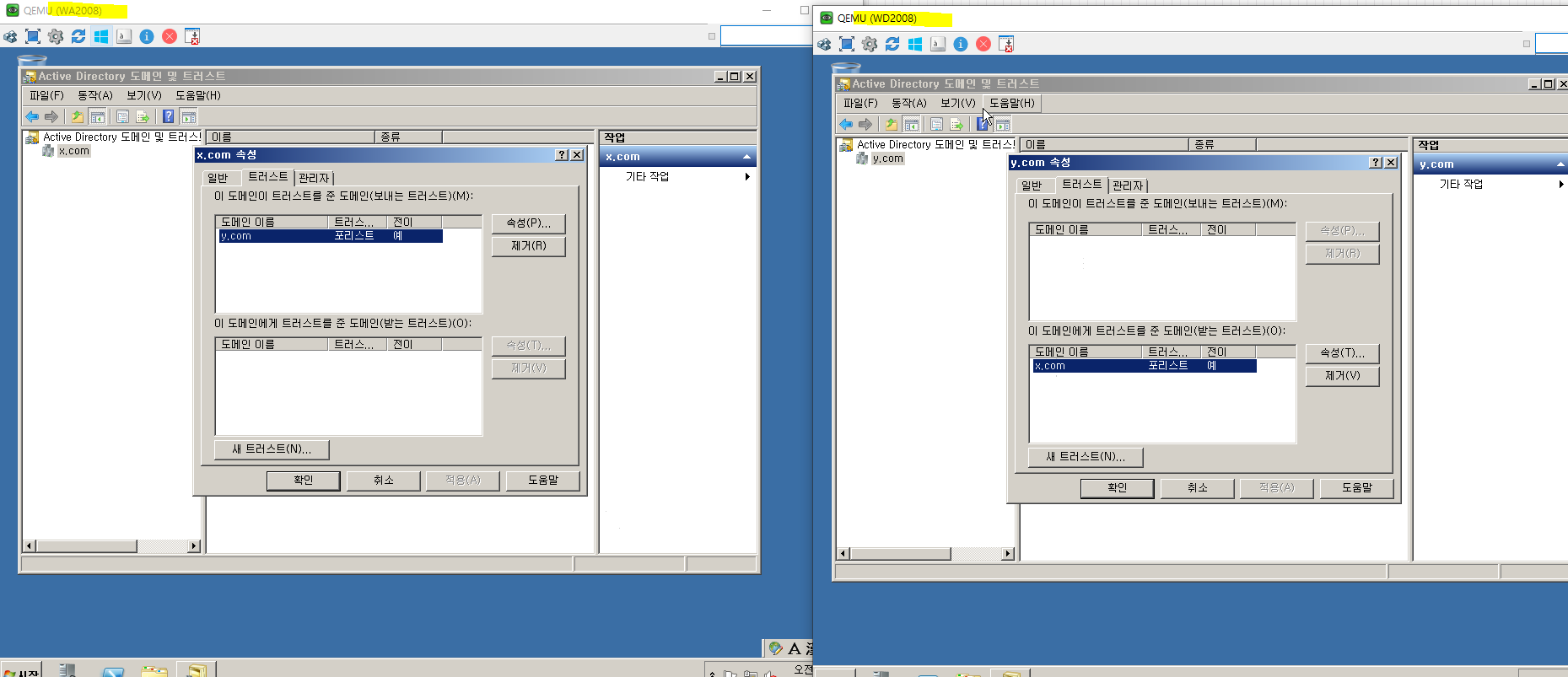
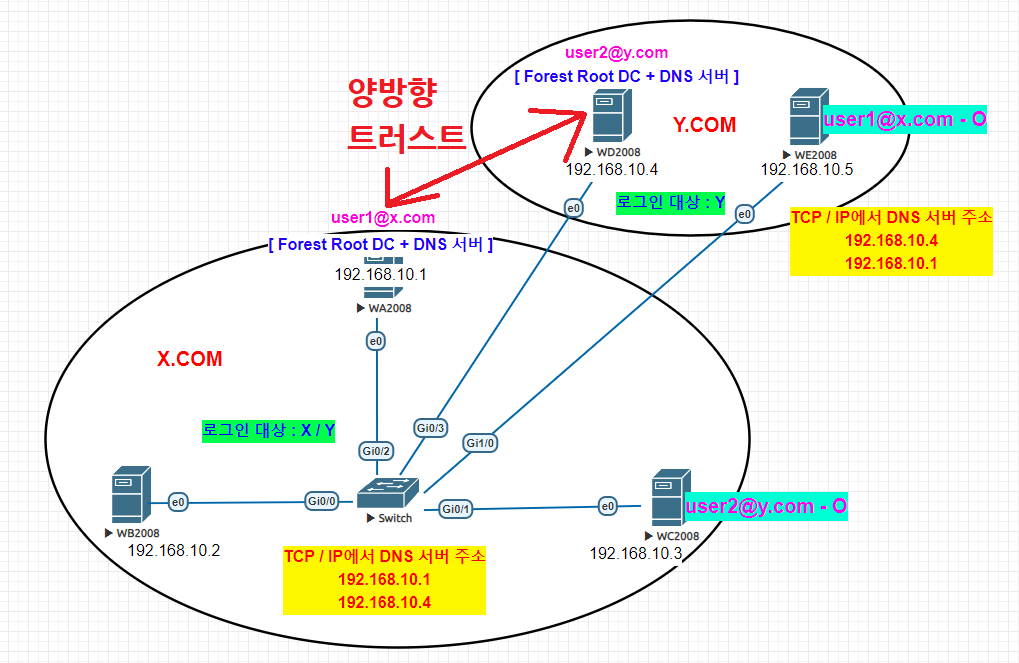
양방향 Trust
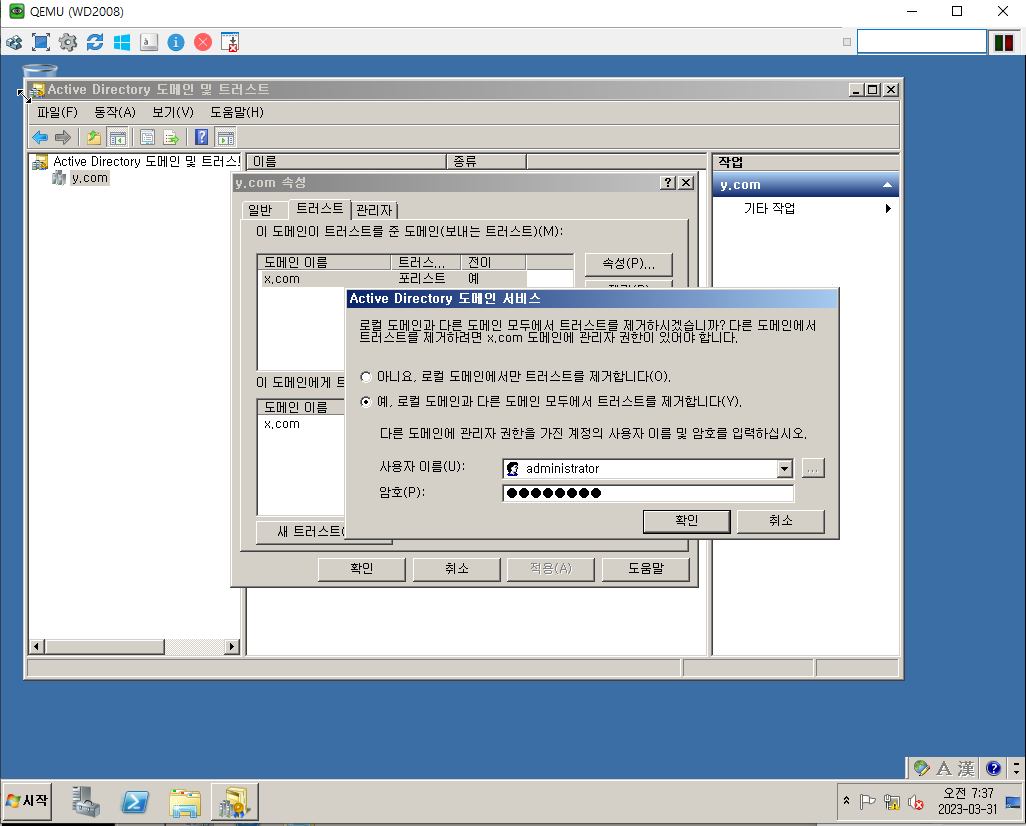
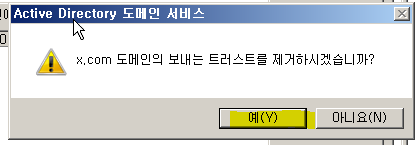
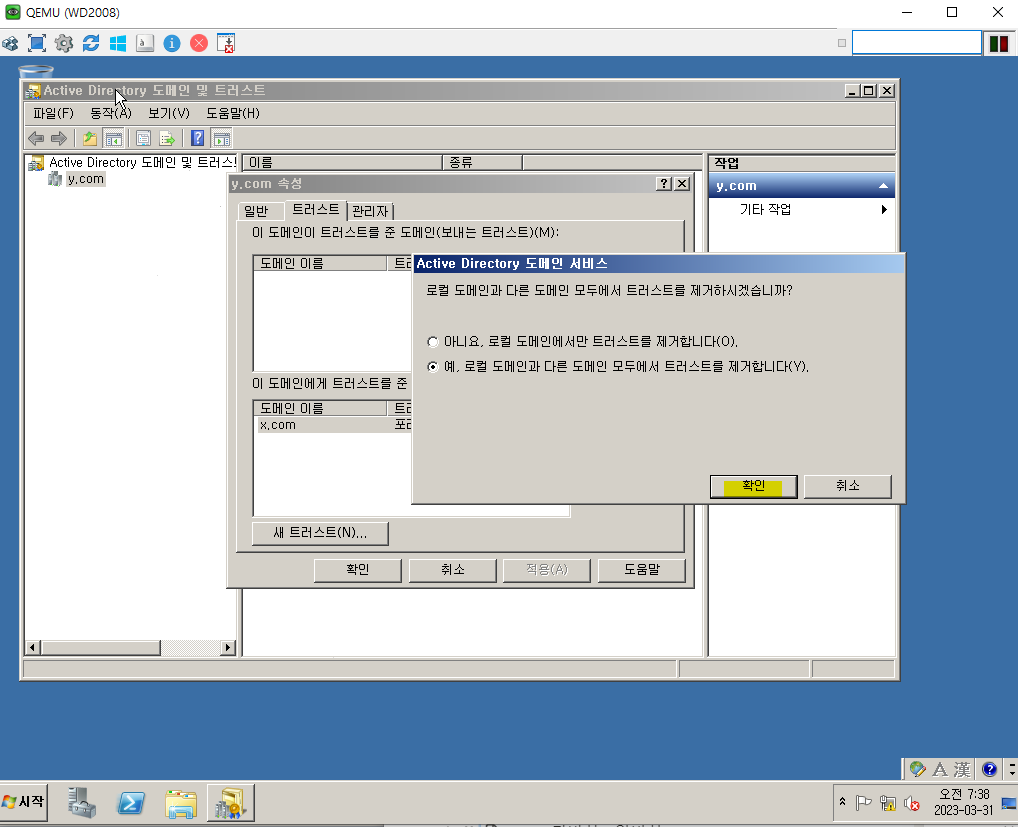
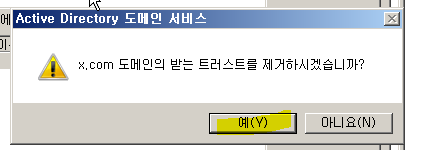
Trust 제거
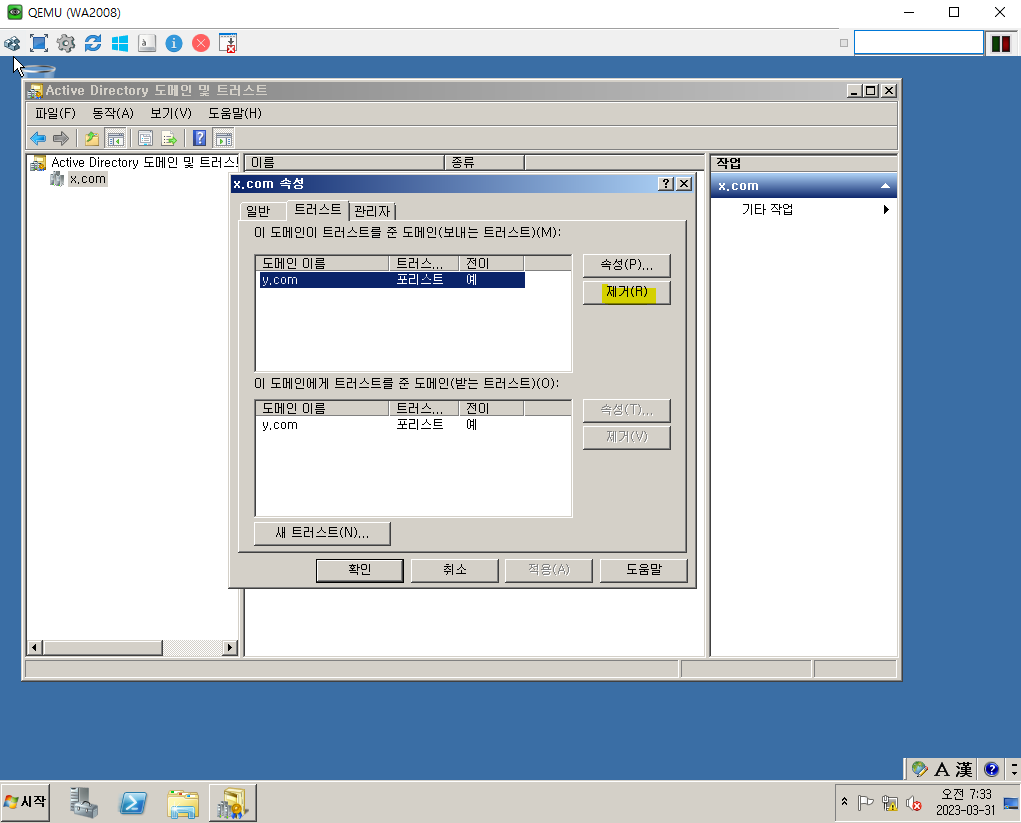
WD